Class-8 – physics
Chapter 2 – physical quantities and measurement
(A)
Fill in the
blanks:
1.
Volume
2.
Volume
3.
Volume

6.
1000
(B)
True or
false
7.
False 8. True
9.
False
10.
True
11.
True
(C)
Tick the
best choice
12.
(d) all of these are
true
13.
(c) (a)and(b)
14.
(a) sinks
15.
(c) partially floats
16.
(b) balances the
weight of that much portion
(17)
Define
1.
The law of
floatation: If the weight of the body is
equal to the weight of the liquid displaced
by it then the body floats in the liquid.
2.
Apparent
weight of a floating body: when any object is
immersed in water then it appears to lose the
weight, this lose in weight is called an apparent
weight of a floating body.
3.
Density of a
liquid: Density of liquid is the ratio of mass
of liquid to the volume of liquid.
4.
Relative
density: Relative density of a substance is
defined as the ratio of the density of the substance
to the density of water at 4℃.
5.
Specific
gravity: Density of a substance when compared to
density of water is known as specific gravity.
18. Match
the following:
Column A
Column B
1.
Relative density
1.
Number
2.
Sinks in water
2.
Iron
3.
Floats in water
3.
Plastic
4.
Density
4.
gcm-3
Answer in
few words:
Q19. How
does the density of a fluid vary with temperature?
Ans. Density of a substance
decreases with the increase in temperature and
increases with the decrease in temperature. Water is
an exception to it.
Q20.
Describe an experiment to measure the density of a
piece of iron?
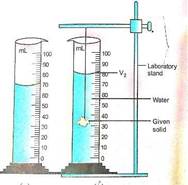
Ans. An Experiment to
measure the density of piece of iron is as follows:
1.Meaure the mass of the
iron piece using a common beam balance. Let it be M
gram.
2.
Fill measuring
cylinder partly with water. Let the level of water
be V1 ml.
3.
suspend the given
iron piece with the thread and gently immerse the
iron piece in water such that no water splashes out
of measuring cylinder. Let the level of water be V2
Ans. 1. Measure the mass of
empty beaker using a common
beam balance. Let the mass be M1
gram.
2.
Put the given liquid
in a measuring beaker up to a
certain level. Let the volume of the liquid
be V ml.
3.
Put liquid into the
empty beaker. Measure its mass
again. Let it be M2 gram.
4.
Result: mass of the
liquid M= (M2 – M1) gram.
5.
Find the density of
liquid using the formula:-
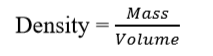
Q22. What do
you know about the density bottle?
Ans.
It is a small bottle having a plug at its
neck. This bottle can store a definite volume of a
liquid. Normally the volume of bottle is 20ml to
100ml. The plug has a narrow opening through it.
Excess liquid overflows through the hole. The bottle
will have the same volume of liquid whenever it is
used.
Q23. What is
the unit of relative density?
Ans. Relative density is the
ratio of same type of quantities so it has no unit.
Q24.A piece
of wood floats on water while an iron nail sinks in
it. Why?
Ans. A
small piece of wood will float on water because the
density of wood is less than the density of water.
An iron nail will sink in water because the density
of iron is more than than the density of water.
Q25. Why
does ice floats in water?
Ans.
Density of ice is 0.9gcm-3 and the
density of water is 1gcm-3 as the density
of water is less than the density of water so it
floats in water.
Q26. Why
does the icebergs floating
on the sea
water
dangerous for the ships?
Ans. An
iceberg floats in sea water with its major portion
under the water. Only small portion of it remains
above the surface of water. A ship can strike the
part of iceberg under the surface of water, damaging
the ship.
Answer the
following questions in detail:
Q27.
What
is density? How is it denoted? Give a relation for
the same. Give unit of density.
Ans. The
density of a substance is defined as mass per unit
volume of the substance.
Density of a
substance is denoted by D.

Q28. Briefly
explain as to how will you workout the density of
regular solids.
Ans.
Knowing mass M and volume V, density of a regularly
shaped substance is given by the
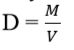
Volume V of the regular
solid is worked out by using the standard formula.
For example:
I.
Volume of cube =
(side)3
II.
Volume of cuboid =
length×breadth×height
Q29.
Describe
different types of vessels for measuring the volume
of liquids.
Ans. We
make use of different vessels for measuring the
volume of liquids.
Measuring
cylinder: It is made of some transparent
material like glass or plastic. It is graduated in
millitre(ml) which increases from zero at the
bottom. Measuring cylinders are available in
different capacities from 20ml to 1000ml.

Measuring
jug: Measuring jugs can be made of glass,
plastic or metal. They are used to measure a fixed
volume of liquids. These are commonly used by milk
sellers, petrol pumps, oil dealers etc.
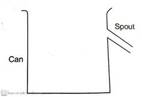
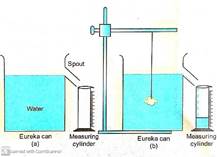
Eureka can:
It is also known as density can. It is made of
glass, plastic or metal. It has opening near its top
called spout.
Q30.
How will you
find the density of an irregular solids: (1) using
measuring cylinder (2) using Eureka can.
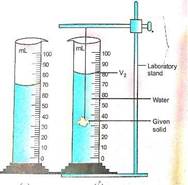
Ans. To
measure the density of an irregular solids using
measuring cylinder follow these steps:
I.
Measure the mass of
the solid using a commom beam balance. Let it be M
gram.
II.
Fill the measuring
cylinder partly with water. Let the level of water
be V1 ml.
III.
Suspend the solid
with a thread and gently immerse the solid in water
such that no water splashes out of
measuring cylinder. Let the
level of water be V2 ml.
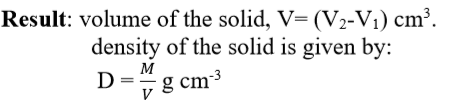
I.
Keep the measuring
cylinder under the spout of Eureka can. Pour water
in the Eureka can till it starts overflowing through
the spout.
II.
Wait till water stops
dripping.
III.
Remove the measuring
cylinder and dry it. Put it again under the spout.
IV.
Immerse the solid
gently into the water in can. The displaced water
overflows through the spout to the measuring
cylinder.
V.
When water dripping
through the spout, note the volume of water in the
measuring cylinder. Let it be V cm3. Now,
measure the mass of the given solid with a common
beam balance. Let it be M gram.
Volume of soild = volume of water in
measuring
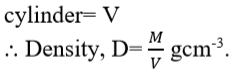
cy
Q31. How
will you measure the density of a liquid with the
help of measuring vessel.
Ans. 1.
Measure the mass of empty beaker using a common beam
balance. Let the mass be M1 gram.
2.
Put the given liquid
into a measuring beaker up to a certain level. Let
the volume of the liquid be Vml.
3.
Put the liquid into
the empty beaker. Measure its mass
again. Let it be M2 gram.
4.
Result:
mass of the liquid M=(M2-M1)
gram.
find the density of the liquid using the
formula:
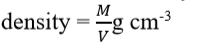
Q32.
What is
density bottle? how will you use it to find the
density of a liquid using a density bottle?
Ans. A
density bottle is a bottle of known volume which can
be weighed empty and then with the liquid, density
of which is to be found.
To find the density of
liquid using density bottle using a density bottle
follow these steps:
1.Take mass of an empty dry
density bottle by using a beam balance. Let it be M1
gram.
2.
Fill the bottle with
water and insert the stopper. The excess water
overflows through the opening of the stopper. Dry
the outer body of bottle with wipping cloth. Measure
the mass of bottle. Let it be M2 gram.
3.
Empty the bottle. Dry
it. Fill it with the given liquid. Insert the
stopper.the excess liquid, will overflow through the
opening of the stopper. Dry the outer part of the
body of the bottle with wipping cloth. Measurebthe
mass of bottle. Let it be M3 gram.
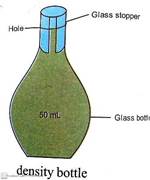
Result:
Mass of water= (M2-M1)
gram
Mass of liquid=(M3-M1)
gram

Q33.
What is the
differnce between relative density and specific
gravity? Discuss densities of three states of
matter.
Ans. The
relative density of a substance is defined as the
ratio of the density of the substance to the density
of a standard or reference material may be water.
Standard or reference material may be water. Density
of water is given a special name called specific
gravity. A subsatnce is dense in solid state, less
dense in liquid state and rarer in gaseous state.
Q34.
Discuss the
concept of floating and sinking.
Ans. An
object in a liquid, floats
if its density is less than the density of
liquid. It sinks in a liquid
if its density in a liquid is more than the
density of liquid.
Q35. State
the principle of floatation. Show that an object
floats with its portion more outside the surface of
a liquid having higher density than water.
Ans.
Principle: If
the weight of a body is equal to the weight of
liquid displaced by it then the body floats in
liquid.
Procedre:
1.
Mark I and II on the
blocks. Take water in a beaker A and glycerine in
beaker B.
2.
Place gently the
block II on the surface of water in beaker A and the
block II on the surface of glycerine beaker B.
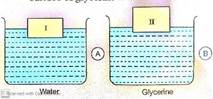
Observation:
Block I floats
in water with its portion outside the surface
lesser than the block II.
Result:
1.The density of glycerine
is more than the density of water.
2. The density of wood is
less than the density of water and the density of
glycerine also.
Q36.
Discuss
various applications of law of floatation.
Ans.
Various applications are:
1.
Ice floats
in water: one tenth part of ice remains outside
the water and the rest inside the water as the
density of ice is 0.9gcm-3 and the
density of water if 1gcm-3.
2.
Swimming
in sea water:
The sea water contains salt. So, its density is more
than the density of river water. Sea water gives
more upthrust to the swimmer than river water.
3.
Floating
submarine: It is a special boat which can travel
under water. It has water tank these tanks are
filled with water so that the density of the
submarine becomes more than the density of sea water
so it sinks. When these tanks are emptied then, the
density of submarine becomes less than the density
of sea water, and the submarine rises to the surface
of the water.
4.
Sailing of
ship: A ship made of iron does not sinks but a
nail does. The density of nail is greater than that
of water. But, the hollow space of ship contains
air. Thus, the average density of ship is less than
that of water so it floats.
Numericals
Q37. The
density of a substance is 3.2g cm-3.
Express it in kg m-3.
Sol. The
density of a substance = 3.2g cm-3
As we know 1
g cm-3= 1000kg m-3
Density = 3.2×1000 kg m-3
=
3200kg m-3.
Q38. A piece
of iron mass 500gram has a volume of 64cm3.
Calculate the density of iron.
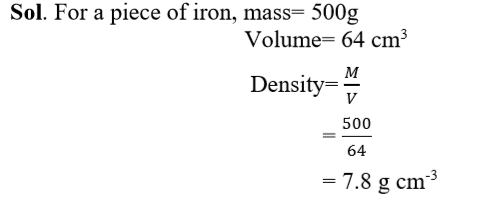
Q39.
Find the
density using the data given in the table:
|
(a)
mass
of solid
(b)
initial volume of water in measuring
cylinder.
(c)
final volume of water when solid is
completely immersed in water.
|
70g
25ml
40ml
|

Q40.
The mass of
empty density bottle is 20 gram, when filled
completely with water it weighs 65 gram and 75 gram
when filled completely with a liquid.
Find the
relative density of liquid.

Q41. Use
the following data to find the density of the
liquid:
|
Mass of empty
density bottle
Mass of bottle+water
Mass of
bottle+liquid
|
20gram
60gram
70gram
|
Sol.
Mass of empty density bottle = 20g
Mass of bottle + water = 60g
⸫ mass of water
= 60-20
= 40g
Mass of bottle + liquid =
70g
⸫ mass of liquid = 70-20
= 50g
If density of water = 1g cm-3
Then, mass of water = volume
of water= volume of liquid.
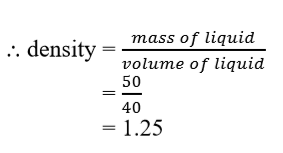
Chemistry, Lesson- 2 (Physical and Chemical changes)
OBJECTIVE
QUESTIONS-(answers)
1)
d- the burning of LPG
2)
a- the changes of the
phases of moon
3)
b- sublimation
4)
c-photosynthesis
5)
b- freezing of water
FILL IN THE BLANKS-
(answers)
1)
does not changes
2)
chemical
3)
endothermic
4)
water vapour
5)
moisture
6)
increases
TRUE/FALSE-
1)
false (a physical
change is reversible)
2)
false (a chemical
change is irreversible)
3)
true
4)
true
5)
true
6)
false (the slaking of
lime is an exothermic change)
SHORT QUESTIONS-
1Q- What are reversible
changes? Which of the two- the vapourisation of
water and the burning of paper -is a reversible
change?
Ans- The changes which can
be reversed, that is the product formed as a result
of change can be converted back into its original
form, are called as reversible changes. The
vapourisation of water is an example of a reversible
change.
2Q-What are irreversible
changes? Which of the two- the melting of ice and
the growth of a plant - is an irreversible change?
Ans-The changes which cannot
be reversed, that is the product formed as a result
of change cannot be converted back into its original
form, are called as irreversible changes. The growth
of a plant is an example of an irreversible change.
3Q- Define a periodic
change. Is rusting a periodic change?
Ans- The changes which occur
again and again at fixed intervals of time are
called as periodic changes. Rusting is not a
periodic change because it is a chemical change
which cannot be reversed or repeated.
4Q- Define a non-periodic
change. Is the swinging of a pendulum a non-periodic
change? Ans- The changes which do not occur at fixed
intervals of time and can occur at any time are
called as non-periodic changes. The swinging of a
pendulum is not a non-periodic change,but a
periodic change because it
repeats at fixed intervals of time.
5Q- Classify the following
into desirable and undesirable changes. Ans- (a) the
spoiling of food- undesirable change
(b)
the digestion of
food- desirable change
(c)
the rotting of an
egg- undesirable change
(d)
the decay of a dead
animal in open air- desirable change
6Q- Define a physical
change. Is rusting a physical change?
Ans- The change in which no
new substance is formed and which can be reversed by
reversing back the conditions, is called a physical
change. Rusting is not a physical change, but a
chemical change because a new substance is formed in
it and it cannot be reversed.
7Q- Define a chemical
change. Is the heating of an electric iron a
chemical change? Ans- The change in which a new
substance is formed and which cannot be reversed
back by reversing the conditions, is called a
chemical change. The heating of an electric iron is
not a chemical change, but a physical change because
after heating it only gets hot and is still
chemically the same iron.
8Q- Classify the following
into physical and chemical change. Ans- (a) the
melting of ice- physical change
(b)
respiration- chemical
change
(c)
the cooking of food-
chemical change
(d)
fermentation-
chemical change
(e)
the evaporation of
liquid- physical change
(f)
the sublimation of
iodine- physical change
(g)
the dissolving of a
solid- physical change
(h)
the burning of coal-
chemical change
(i)
the glowing of a
bulb- physical change
(j)
the freezing of
water- physical change
(k)
the curdling of milk-
chemical change
(l)
photosynthesis in
green plant- chemical change
(m)
the condensation of
water vapour- physical change
(n)
the digestion of
food- chemical change
9Q- Define exothermic and
endothermic changes.
Ans-
Exothermic changes-
The changes in which heat is evolved are called as
exothermic changes. Eg- freezing of water.
Endothermic changes-
The changes in which heat is absorbed are called as
endothermic changes. Eg- melting of ice.
LONG QUESTIONS-
1Q- Give two examples to
show that the mass of the individual substance (s)
undergoing a chemical change is altered. How do
these changes obey the law of conservation of mass?
Ans- Law of conservation of mass states that matter
can neither be created nor be destroyed but can only
be transformed from one form to another. The mass of
the individual substances undergoing a chemical
change is altered,but they do obey the law of
conservation of mass. For eg-
1)
Burning of coal-
When a coal is burnt in air, the mass of the soot,
ashes and gases evolved, equals to the original mass
of the coal and the oxygen when it first reacted.
So, the mass of the product equals the mass of the
reactant.
2)Cellular
Respiration- It also follows the law of
conservation of mass because it arranges the atoms
of glucose and oxygen to make carbon dioxide, water
and energy. The total amount of mass of glucose and
oxygen (reactants or inputs) and the total amount of
mass of carbon dioxide, water and energy (products
or outputs) is equal.
2Q- State the difference
between a physical and a chemical change.
Ans-
|
PHYSICAL CHANGE
|
CHEMICAL CHANGE
|
|
1) A physical change
is temporary
|
1) A chemical change
is permanent.
|
|
2) A physical change
is reversible
|
2)A chemical change
is irreversible.
|
|
3) No new substances
are formed in a physical change.
|
3)New substances are
formed in a chemical change.
|
|
4)The mass of
substance does not change in a
|
4)The
mass
of
individual
substances
|
|
physical change.
|
undergoing a
chemical change are altered.
|
|
5)Eg- melting of
ice.
|
5)Eg- burning of
coal.
|
3Q- Discuss an example to
show that physical and chemical changes can occur
together. Ans- Physical and chemical changes can
occur together. This can be proved by taking the
example of burning of a candle. When a candle burns,
following changes occur-
Physical change-
the wax under the wick gets heated and melts. The
molten wax flows down and solidifies. Thus the
change in state is from solid to liquid and again
from liquid to solid, which are physical changes.
Chemical change-
a part of the molten wax vaporizes and burns to form
new substances, carbon dioxide and water vapour.
This change is irreversible. So burning of wax is a
chemical change.
4Q- Give one example of each
kind to show that a change in energy takes place
when a physical or a chemical change occurs.
Ans-- Energy changes are
observed when a physical or a chemical changes
occurs.
1)
Energy changes in a
physical change-
Eg-Melting
of a solid- When a solid melts heat is
absorbed,hence energy increases.
Freezing of a
liquid-When a liquid freezes heat is
evolved,hence energy decreases.
2)
Energy changes in a
chemical change-
Eg-
Burning of coal-
When a coal or wood is burnt, heat and light are
emitted. So, burning is an exothermic process.
5Q- Explain why there is an
energy change in a change of state of matter as well
as in a chemical change.
Ans- Energy changes in change of state of
matter-
Energy is always involved in
changes of states. Matter either loses or absorbs
energy when it changes from one state to another.
For eg- when a matter changes from a liquid state to
a solid, it loses energy. The opposite happens when
matter changes from a solid to a liquid.
energy increases
energy increases
SOLID
 LIQUID
LIQUID
 GAS GAS
energy decreases
energy decreases
Energy changes in a
chemical change-Chemical changes often involve
changes in energy due to the breaking and formation
of bonds. Changes in which energy is released or
evolved are exothermic changes, while those that
take in heat or absorbs heat are endothermic.
Class
8 English
CH-1 THE ADVENTURE OF THE BLUE CARBUNCLE
Ans1) Holmes exclaimed that as the hat was very large so the
owner of the hat must have some brain and there were
some fine grey hair on the lining of hat. He added that
the hat had a fine whiff of lime. With the help of all
these facts he made it clear that the man was clever,
middle-aged and used lime cream in his hair.
Ans2) Mr Baker came to see Mr Holmes as he had given
advertisement in the newspaper about the goose and a
hat. So, being the owner of the goose and hat, he came
to meet Mr Holmes to take the things back.
Ans3) Mr Holmes watched that the goose seller was shaking his
fists at a rat faced man who was whining that the goose
was his, Mr Holmes followed that man and said that it
might save his visit to Brixton road.
EXERCISE [ D ]
Ans1) Mr Oakshott must have felt very sad as Mr Ryder was her
brother and in addition to that particular goose had
come from her. Mr Ryder had put the stolen gem into the
mouth of that goose. He thought that his sister had
reserved the same goose for him and thus hoped to avoid
being caught red-handed.
Ans2) Mr Ryder might have been arrested by the police as he
did a big crime by stealing the precious gem from the
counter of Morcar.
Ans3) 1. Mr Ryder: Mr Ryder was a hotel attendant. He
was not a truthful person and moreover he was not
sincere to his duty. He stole the gem and blamed the
plumber for the theft.
2. Mr Baker: Mr Baker was the owner of the
goose. He was very honest and truthful. He was not
responsible for the theft of the gem.
3. Mr Holmes: He was sincere detective. He
was very intelligent, active and devoted to his duties.
He always took interest in solving the causes of crime.
4. Dr Watson: He was the friend of Mr
Holmes. He was originally a military doctor who served
in the army. He is intelligent but lacks the power of
Holmes’s skills of deduction.
POEM – I REMEMBER ……I
REMEMBER
EXERCISE- C
Ans3) The poet wants the night to be long so that he does not
have to wake up to the harsh reality where he was sad
and melancholic.
Ans4)
A beautiful garden with many flowers- roses,
lily-cups and lilac surrounded his house. There was a
fir and laburnum tree as well along with swings.
Ans5) As a child the poet was carefree, he had no troubles and
could feel happy in the little pleasure of life. Hence
the poet says that his spirits flew he was young.
Ans6) As the child uses the swing, he realizes the way birds
would feel in the fresh air.
Ans7) When the poet was a child, he thought the trees were
tall enough to touch the sky and hence were closer to
God.
Class-8 Representation of Geographical Features
Exercises
1.
Fill in the
blanks
(a)
Nucleated
(b)
Col
(c)
Far apart
(d)
Same
elevation
(e)Ridge
2.
Match the
following
A – 2
B – 1
C – 3
D – 5
E – 4
3.
Write “T”
for True and “F” for false
(a)
True
(b)
False
(c)
True
(d)
False
(e)True
4.
Answer the
following questions briefly
(a)
Maps that
show natural and man-made features with the help of
colours and conventional signs (symbols).
(b)
Contours are
lines on a map that join the same height above or below
sea level. We always use brown colour to show contour
lines.
(c)
Spacing of
contours indicate the slope or gradient of the landform.
Closely spaced contours represent steep slopes while
widely spaced contours represent gentle slopes.
(d)
The common
signs including letters that are used for representing
various natural and man-made features are called
conventional signs. These are universally accepted.
(e)The
following geographical features are formed by contours:
Waterfalls or cliffs, conical hills, plateaus, ridges,
gaps, saddles, cols and passes.
Important
Terms
Settlements
Settlements
are towns and villages where basic infrastructure
services like water, electricity and roads are provided.
Types
of Settlements
1.
Linear
settlements are settlements where the buildings are
constructed in lines, often next to a lake shore, river
or following a road.
2.
Nucleated
settlements are ones where the houses are grouped
closely together, often around a central feature like a
church, pub or village green.
3.
Dispersed
settlements are ones where houses are scattered over a
wide area.
4.
Radial
settlements are where the dwellings spread out in
several directions from a central point, which is either
around a big water body or where many routes join
together.
Class 8 English A Tale of Two Cities
Chapter 2
Exercise : A
Ø Dickens describes the poor men in Streets of
Paris as scarecrows because they were in worst
condition and starved to death.Their clothes
Were ragged badly and were hung on their bodies
like the scarecrows in the fields.
Ø It was tough time in France and no one from
other countries was allowed to move freely.It
was not safe for the native people .Therefore
Mme Defarge was keeping a watchful eye in the
café on each and everything that was going on so
that no stranger could enter.
Ø I listen to the music whenever I feel
distressed.It gives me relaxation and comfort. I
like to listen music on radio or television.
Exercise : B
Ø Mr Defarge means to say that he used to make a
show of Dr Manette to a chosen few . He said
that these chosen few were the real men who had
the sympathy for humanity, he added that being
an English,Mr Lorry could not understand the
sufferings of the people of France.
Ø When Miss Manette sat beside Mr Manette ,he
took out the ragged string which he had tied
around his neck.He unfolded it and found four
hair that were as same as the hair of Miss
Manette .He was astonished and couldn’t
recollect if ever he had met Miss Lucy in his
past life.
Ø Dr Manette was having a defeated soul now.He
had forgotten everything about his past life and
did not even remember his own real name.He could
not recognise his own daughter and his friend
His body was like a skeleton with thin layer of
skin covering it.
Class 8 (Physics)
MATTER (25-31)
Q26. Why do wet clothes don not dry easily on rainy
day?
Ans. Wet cothes do not dry easily on a rainy day
because quantity of water vapours in air is more, so
the evaporation becomes slower in damp air.
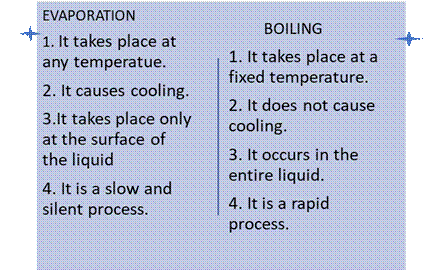
Q27. Compare evaporation and boiling.
Q28.Tabulate the properties of solid, liquid and
gaseos state of matter.
Ans.
|
CHARACTERISTICS
|
SOLIDS
|
LIQUIDS
|
GASES
|
|
1.NATURE
|
Hard and rigid
|
Fluid
|
Highly fluid
|
|
2. SHAPE AND VOLUME
|
Definite shape and volume
|
Indefinite shape abd definite volume
|
Indefinite shape and volume
|
|
3.INTERMOLECULAR SPACES
|
Very small
|
Comparatively large
|
Very large
|
|
4.ARRANGEMENT OF PARTICLES
|
Closely packed
|
Loosely packed
|
Very loosely packed
|
|
5. COMPRESSIBILITY
|
Negligible
|
Very small
|
High
|
Q29. With the help of an activity, describe the
phenomenon of sublimatioon.
Ans.
1.
Put napthalene balls in a china dish.
2.
Invert glass funnel over the china dish.
3.
Plug the stem of funnel with cotton.
4.
Slowly heat china dish and observe,
5.
we will observe that napthalene changes directly
into gaseous state, Napthalene thus sublime on
heating.
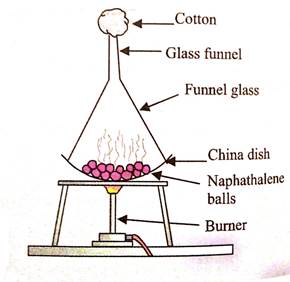
Q30. Define the process involved in change of state
due to heating.
Ans.
●
BOILING
:- Boiling is the process by which liquid turns into
a vapour when it is heated to its boiling point.
●
VAPOURISATION
:- It is defined as the change from liquid statte to
gases stateon heating at particular temperature.
Vapour is a gases state of the substance.
Q31. Define the process involved in change of state
due to cooling.
Ans.
●
CONDENSATION :- It is a process of changing the
gaseous state of a substance into liquid stateon
cooling.
●
FREEZING :- It is a process of changing gaseous
state of substance into liquid state on cooling.
Class 8 Biology Chapter
1st'Transport in plants'
Exercise A Fill in the
blanks
1.
Diffusion
2. Semipermeable
3. Hypertonic
4. Low, higher
5. Carrier proteins
6. Tracheids, vessels
7. Phloem
8. Phloem fibre
9. Transpiration
10. Lenticels, cuticle
11. Calcium
12. Iron, nitrogen
B. Choose the correct option
1.(d)
2.(b)
3.(a)
4.(b)
5.(c)
6.(b)
7.(d)
8.(d)
9.(c)
10.(d)
C.Match the following
1.d
2.e
3.f
4.h
5.c
6.a
7.b
8.g
D.Answer the following questions
1.Diffusion is a process in which particles of a
substance moves from an area of higher concentration
to an area of lower concentration until they are
evenly distributed.
For example:
(a)Plants absorb minerals by diffusion.
(b)Diffusion helps in gaseous exchange between
plants and atmosphere.
(c)The release of water vapours through the stomata
in plants takes place through diffusion
2.Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules
through a semipermeable membrane from an area of
higher concentration to an area of lower
concentration.
(a)Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules
while diffusion is the movement of particles like
solid,liquids and gaseous.
(b) In osmosis semipermeable membrane is required
while in diffusion there is direct movement of
particles.
3.Active transport is the movement of molecules
against the concentration gradient from an area of
lower concentration to an area of higher
concentration. This process requires expenditure of
energy.
4. Xylem is made up of four type of cells:
(a) Tracheids
(b) Vessels
(c) Xylem parenchyma
(d)Xylem fibres
Phloem also has four types of cells:
(a)Seive tubes
(b)Companion cells
(c)Phloem parenchyma
(d)Phloem fibres
5.Transpiration is the process by which plants
release water in the form of water vapour.
6. Transpiration creates transpiration pull which
helps in the upward movement of water and minerals
in plants.
(a) Transpiration helps concentrate the cytoplasm of
plant cells, which helps in osmosis.
(b) It helps distribute water and minerals
throughout the plant body.
(c)It helps cool the plant body as a lot of heat is
taken up in converting water into water vapour.
7. The three macronutrients required by plants are:
(a) Potassium
(b) Calcium
(c)Nitrogen
Micronutrients are:
(a)Copper
(b)Iron
(c)Sodium
8.(a) Nitrogen-Yellow leaves and slow growth
(b) Phosphorus-Root and shoot are too short and late
flowering
(c)Calcium-Death of tissues and weak stem.
(d)Iron-Inadequate chlorophyll in leaves.
E. Explain in brief
1.Take a large potato peel it and cut off a slice
from one end to make it flat.Make a deep cavity
within the potato. FIll the cavity with concentrated
sugar solution.Stick a pin into the potato to mark
the level of the sugar solution.Place the potato in
a beaker containing water.After 2 hours observe the
level of the sugar solution within the cavity.We
will see that the level of the sugar solution in the
cavity has risen.Water from the beaker enters a
cavity by osmosis and causes a sugar solution to
rise.(Diagram is on page no.3 1.4a)
2.If we place a cell in hypotonic solution the cell
will get swollen due to endosmosis.If we place a
cell in hypertonic solution the cell will get
flaccid due to exosmosis and if we place the cell in
an isotonic solution there will be no change in the
shape of the cell.
3.Xylem cells are of four
types-tracheids,vessels,xylem parenchyma and xylem
fibres.
(a)TRACHEIDS:These are elongated, tubular cells with
tapering ends and thick lignified walls. Tracheids
are dead cells.
(b)VESSELS:These are also dead, elongated, tubelight
structures with lignified walls. Vessels are made of
cells called vessel elements.
(c)XYLEM PARENCHYMA:These aa living parenchymatous
cells that help conduct water and also store food.
(d)XYLEM FIBRES: These are dead sclerenchymatous
cells that provide mechanical strength to the
tissue.
Diagram is on page 5 fig.1.8
4. Phloem has four types of elements:
(a)SEIVE TUBES:These are slender, elongated,
tubelight cells placed end to end. Seive tubes are
living cells, but they lack nuclei. Sieve tubes have
seive plates
through which food is transported between cells and
finally to all parts of the plants.
(b) COMPANION CELLS: Thesecells are found beside
seive tubes and are connected to them through pores.
The cells assist seive tubes in the conduction of
food.
(c) PHLOEM PARENCHYMA: These are living cells. The
cells store food and also help conduct it.
(d) PHLOEM FIBRES: These are dead sclerenchymatous
cells that provide mechanical strength to the phloem
tissue. The cells are also called bast fibres.
Diagram is on page no.5. fig.no.1.9
6.Take a healthy, well watered potted plant and
cover the pot with a rubber sheet or a larger
polythene bag.Place the potted plant in sunlight and
cover it with the bell jar to make it airtight.After
a few hours we will see that moisture has
accumulated on the inner wall of the bell jar due to
water vapours released during transpiration. This
shows the process of transpiration in plants.
5.The concentration of glucose increases within the
guard cells during the day and the drawing water
from the surrounding cells by osmosis. As a result
they bulge outwards, opening the stomach and
allowing water vapour to escape from the underline
intercellular spaces. In this way transpiration
occurs in plants.Transpiration stops when the
stomata close during the night.
The factors that affect transpiration in plants are:
(a) Intensity of light
(b) Temperature
(c) Humidity
(d) Atmospheric pressure
(e) Velocity of wind
7.The active transport of minerals into the root
cells increases the concentration of their
cytoplasm, does promoting absorption of water by
osmosis. The entry of more and more water into the
xylem vessels creates an upward pressure called root
pressure, which pushes the sap upward in the stem.
8.Take a potted plant and water it well. Using a
knife, cut off the stem a few inches above the
soil.Fix a long narrow glass tube to the cut end of
the stem with the help of rubber tubing. Pour a
little coloured water into in the glass tube and
mark its level.Pour a little oil over the coloured
water to prevent evaporation. Use clamp with stand
to hold the glass tube straight. After sometime we
will find that the level of coloured water into the
glass tube has risen. The root pressure pushes the
coloured water in the tube and causes it to rise.
COMPUTER
Class 8 CH
– 1(OS & GUI) - Roles and Functions
1.
Tick the correct answer.
a.
User Interface
b.
Hard Disk
c.
Interface
d.
Booting
e.
Device driver
f.
Multiprocessing
g.
Solaris
2.
True and False.
a.
T
b.
F(does not /does)
c.
T
d.
T
e.
F(Novell’s Netware/BOSS)
f.
T
g.
T
h.
F(Difficult /easy)
3.
Fill in the blanks.
a.
Bridge
b.
Warm boot
c.
Mac OS X
d.
Multiuser
e.
Stand alone
f.
Server
g.
Command
h.
Touch
4.
Define the following
a.
Multitasking OS
– A multitasking operating system allows a single user to
work on two or more applications that reside in memory at
the same time.
b.
Multiprocessing OS
– A multiprocessing operating system can support two or more
processors that run programs at the same time.
c.
Real time OS
– A real time operating system (RTOS) is an operating system
that guarantees to work within a specified time limit.
d.
Distributed OS
– A distributed operating system is a network –based
operating system which is carried out on more than one
machine.
5.
Answer in 1-2 sentences.
a.
What is a Software ?
Ans.
Software consists of a series of related
instructions, organized for a common purpose,
that tells the
computer what tasks to perform and how to perform.
b.
What is the role of Operating System ?
Ans. Operating system acts as an interface between a
user and the hardware. It also hides the complexity of the
hardware from the user.
c.
How many categories of Operating system are used ? Name them
Ans. There are three basic categories of Operating
System .
1. Stand- alone Operating System.
2. Server Operating System.
3. Embedded Operating System.
d.
Differentiate between Stand-alone OS and Server OS .
Ans.
|
Stand-alone OS
|
Server OS
|
|
1.
An operating system that works on
a desktop computer or notebook computer is called a
stand-alone operating system.
2.
Examples- MAC OS X, LINUX.
|
1.
A Server operating system is an
operating system that is designed specifically to
support a network.
2.
Examples- LINUX,UNIX, SOLARIS.
|
e.
What is a User Interface?
Ans. A User
Interface controls how you enter data and instructions as
well as the display of information on the screen.
e.
How many types of User Interface are used ? Name the
f.
Ans. Two types of
user interface are there .
1.
Command Line Interface (CLI)
2. Graphical User Interface(GUI)
g.
Differentiate between CUI and GUI.
Ans.
|
CUI
|
GUI
|
|
1.
In a CUI , a user types commands
or presses special keys on the keyboard to enter
data.
2.
Example- DOS (Disk Operating
System)
|
1.
In a GUI, we interact with menus,
icons and etc. to issue commands.
2.
Example- Mac OS, Ubuntu.
|
6.
Answer Briefly
a.
What are the functions of
operating system ? Explain any three.
Ans. The functions of operating
system are :
1.
Processor Management-
Processor management means managing the program or programs
running on the processor at a given time.
2.
Memory Management- The
purpose of memory management is to optimize use of Random
Access Memory (RAM).
3.
User Interface- A user
interface controls how we enter data and instruction as well
as the display of information on the screen.
b.
Name some popular server
operating systems. Define them.
Ans. Some popular server operating
system are:
1.
WINDOWS SERVER- Developed
by Microsoft, Windows Server enables
organizations to manage
applications and websites.
2.
SOLARIS- It is a version
of UNIX , developed by Sun Microsystems designed for
e-commerce applications.
3.
NOVELL’S NETWARE- It is a
server operating system , designed for client/server
networks.
4.
BHARAT OPERATING SYSTEM
SOLUTIONS(BOSS)- It is an easy- to- use version of Linux,
developed by C-DAC, India.
c.
What is an Embedded
Operating
System ? Give some
examples.
Ans. The Operating system on mobile
devices and many consumer electronics is called a Mobile
operating system or Embedded operating system. These
operating systems reside in the ROM chips. It includes
calendar , contact management, text messaging, email, Touch
screen , digital camera, media player and wireless
connectivity such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
d.
What are the basic
principles while designing User Interface?
Ans.
The
basic principles while
designing User Interface are :
1.
User familiarity – The
interface should be based on user-oriented terms and
concepts rather than computer concepts.
2.
Consistency- The system
should display an appropriate level of consistency.
3.
Recoverability-The system
should provide some flexibility to user errors and allow the
user to recover from errors.
4.
User guidance- Some user
guidance such as help system, on-line manuals, etc should be
supplied.
5.
User diversity- The
interface should provide appropriate interaction facilities
for different types of system user.
e.
What are the advantages of
CLI?
Ans. 1. The user is in direct
communication with the computer.
2.
The user is not restricted
to a number of predetermined options.
3.
It is possible to alter
computer configuration settings.
4. Working on CLI is fast.
f. Write down the characteristics
Of GUI.
Ans. 1. Windows: Multiple windows
allow different information to be displayed simultaneously
on the user’s screen.
2.
Icons: Icons display
different types of information. Some icons represent files
while others represent processes.
3. Menus: Command are selected from
a menu rather than typed in a command language.
4. Pointing: A pointing device such
as a mouse is used for selecting choices from menu
5. Graphics: Graphical elements can
be mixed with text on the same display.
HOME
Class 8
English language
Insert
the correct tense of verbs
in each of the following sentences
:
(1)
I told him why I …. that . (do)
(2) The teacher asked boys whether they ….. the sums.
(solve)
(3) I shall go home during
the vacation so that I …... my brother. (see) (4)My son’s
health was so bad last year that he failed …. the
examination .(take) (5)When I …. him last , I spoke to him
.(see)(6)Although they ….. defeated , they did not lose
heart. (be)
(7)He tried how fast he …
walk .(can) (8) Our teacher taught us that virtue …. its own
reward .(be) (9) Our holy books tell us that man …
mortal .(be) (10) He eats
that he … live. (may) (11) He spoke so fast that I ….. not
follow him .(can) (12) Just as I …. the room , the bell rang
.(enter) (13) Who told you that goats … on grass ?(live)
(14) I shall fire if you …. . (speak) (15) He heard that the
cottage …. for sale. (be) (16) His health has improved since
he …. from
the hills. (return) (17)
Do whatever you …. proper. (think) (18) It is clear that he
…. a
clever boy. (be) (19) The
news
that
the enemey …. approaching alarmed the people. (be) (20) This
is the place where Martin …. . (live) (21) He kept quiet
that he …. please me.(may) (22) He would succeed if he …. .
(try) (23) A great building stood where there …. a cottage
now . (be) (24) However poor a man …. be, he has always
something to be thankful for.(may) (25) He declared that he
…. not believe
it even if he saw it with
his own eyes.(will)
Answers
1.
did 2. had
solved 3. can
see 4. to take 5. saw 6. were 7. could 8.is 9. is 10. may
11. could
12.
entered13.live14.speak15.was16.returned17.think18.is19.was20.lived21.might22.tries23.was24.may25.would
NOTICE
WRITING :
Format:
Heading
:
Must be appropriate to the
event
1 mark
Date
:
½ mark
Time
:
½
mark
Venue
:
Hall/auditorium+ Location
Eg. Sandra Hall, St Lawrence School
½ + ½ Mark
Name
of event
:
War with words (Inter
school debate)
1 mark
For whom
?
Detail of audience
,invitiees
eg. Pupils from class 8 to
10
1 mark
Example
:You are the
Secretary
of the children’s club of
your society. You are planning to celebrate Diwali mela
in your locality. Write a
notice to be put up on the notice board of your society
giving details about the event.
Solution:
THE COLOURS OF CULTURE
Grand Diwali
Mela
The Children’s Club
of the society is organizing Diwali Mela .Details are as
follows:
Venue:
Community Hall
Date: 15th
Ocotober 2020
Time: 9am to 2 pm
Stall Charges: RS 2000/-
There will be a
short cultural programme to showcase the talents of
children. All the members of the society are cordially
invited to participate in the Mela
A sumptuous lunch
awaits you.
Class 8
English Lit.
N0VEL-CLASS-8 TH
CHAPTER-1 RECALLED TO
LIFE
EX.A
ANS 1) The
message Recalled to life means brought back to life. This
message refers to Dr. Manette who was in France and was
recently released from prison. His daughter Lucie Manette
thought he had been dead for the past eighteen years but he
was still alive and had forgotten his past life. Slowly and
slowly Jarvis Lorry and Lucie recalled him to life.
ANS 2) the
story took place in the year 1775 . At that time England and
France were undergoing a period of social turmoil. The
people used to wear loose cloths and avoid wearing tight
clothes. They felt themselves very comfortable in the loose
dresses.
ANS 3) one
or two centuries ago our country was under the rule of
Britishers. The condition of Indians was very pathetic
because the Britishers
were very cruel and unjust. Yes, I would like to have
life then and sacrifice my life to free my country.
EX.B
ANS 1) In
the year 1775 social events brought destruction in two
cities that is London and Paris. In both the cities the
prosperity of the ruling class increased and the same way
the poverty of underprivileged. The king and Queen in both
the cities turned a blind eye to the hardships of the
people.
ANS 2) When it was
revealed to Miss Manette that her father was alive and was
in France she lost her balance. Mr Lorry consoled her by
saying that it was not easy for him to handle these
emotional matters as he was he was a man of business.
ANS 3) Lucie Manette was brought up as an orphan. Her father
had been dead for the last eighteen years but when Mr Lorry
told her that he was still alive and had been in the prison
for last eighteen years. This news was really shocking for
her, she said its cant be true and going to meet the ghost
of her father.
Class 8 CHEMISTRY ( LESSON 1)
SHORT QUESTIONS-
1Q- What are
the three states of matter?
Ans- Solids ,liquids and gases.
2Q- Arrange
solids,liquids and gases in order of increasing
intermolecular space.
Ans- Solids < liquids < gases.
3Q- Arrange the
solids,liquids and gases in order of increasing
intermolecular forces.
Ans- Gases < liquids < solids.
4Q- What will
happen to the kinetic energy of a particle if it is heated?
Ans- The kinetic energy of the particles increases if it is
heated.
5Q- What gives
rise to the pressure of a gas?
Ans- The collision of the particles with the walls of the
vessels give rise to the pressure of the gas.
6Q- In which
state of matter do the particles move the longest distances?
Ans- Gaseous state of matter.
LONG QUESTIONS-
1Q- Explain the melting of ice on the basis of the kinetic
theory.
Ans- The particles constituting an ice only vibrate about
their mean positions. As an ice is heated, the K.E of the
particles increases. With the rising temperature, the
particles vibrate more and more vigorously till they move
away from their fixed positions at a particular temperature
called the melting point of the ice. Thus, an ice becomes a
liquid (water).
2Q- Explain the evaporation of a liquid on the basis of the
kinetic theory.
Ans- The
particles in a liquid are in continuous motion, during which
they collide among themselves. If they collide strongly,
some of the particles may overcome the attractive forces and
may escape from the surface. A liquid evaporates in
this manner.
3Q- Explain the liquification of a gas on the basis of the
kinetic theory.
Ans- In the gaseous state, the particles move very fast,
independently of each other. As the temperature is lowered,
kinetic energy of the particles is also lowered. When the
low energy gaseous particles collide with each other, they
may form bigger lumps or clusters and the gas may condense
into a liquid.
4Q- Explain the freezing of a liquid on the basis of the
kinetic theory.
Ans- As a liquid is cooled, the kinetic energy of the
particles decreases. The particles move shorter and shorter
distances as the temperature is lowered. At the freezing
point, the translatory motion of the particles ceases and
the particles get rigidly fixed. This is how a liquid
changes into a solid.
5Q- State the law of conservation of mass.
Ans- According to the law of conservation of mass, “ Matter
can neither be created nor be destroyed but can be changed
from one form to another form and the total mass of the
substances before and after the change remains same”.
6Q- Describe an experiment to prove the law of conservation
of mass.
Ans- Put a small tube or bottle containing a solution of
barium chloride into a conical flask. Put some sodium
sulphate solution in the flask with
the help of a dropper carefully, ensuring that the
two substances do not come in contact with each other. Close
the mouth of the flask with a cork and weigh the flask. Tilt
the flask and swirl for sometime and weigh it again. You
will find that there is no change in the weight of the
flask.
( with DIAGRAM FROM THE BOOK)
CLASS-8
CHAPTER-3 THE TRIAL
EX-A
Ans 1) People become so excited when someone was about to be
hanged as they wished to see public execution .They were
bloodthirsty and were wild with excitement as Charles Darnay
charged with treason-spying for French-was certain to be
found guilty and therefore condemned to death.They had
excessive interest in human suffering which served as a mean
of entertainment
to them.
Ans 2) Sydney Carton had a great potential but had fallen into
the life of alcoholism. He serves as a legal advisor to
Stryver and looks remarkably like Charles Darnay. His
erratic behaviour surprised Darnay when Darnay tries to
thank him for his assistance in the trial. Darnay is polite
gentleman on the other hand Carton is ill mannered and heavy
drinker. So we don’t like him.
Ans 3) A friend should be good adviser, compassionate and
honest. He must take care of one’s feelings and behaviour
accordingly. He should never reveal secrets and remain
faithful. He must standby his friends during odd times.
EX—B
Ans1) In the court room Miss lucy was also present with her
father and Jarvis Lorry. Dr Manette was having a stunned
expression on his face and was looking very distinguished
gentleman with strikingly with white hair. But when his
daughter addressed him, his expression was softened and it
appears as if he was too young and was proud to have his
daughter.
Ans2) Sydney Carton says these words to Charles Darnay. He is
an orphan who has wasted his life on alcohol. He proves to
be complex character who has no real purpose in life and
does not seem to be in the good looks of anyone.
Ans3) These words were spoken by Mr Stryver to Sydney Carton.
He said that he felt sorry for Carton because earlier in
student life, he used to be much better at law than Stryver.
But now he working under Stryver and earning a clerk’s wage.
He felt sympathy for him.
English language
Class 8 A Comprehensive Grammar Of Current English
Chapter17 -
The Participle
Exercise1
1.
Seeing: present
participle: used to express an earlier action of subject.
2.Being disappointed :present participle; used to
express an earlier action of subject.3. Haunted: past
participle: used as adjective, qualifies house.4. Rolling :
present participle, used as adjective, qualifies sstone5.
Being occupied: present participle used to express earlier
action of subject.6.Being closed: present participle, used
to express an earlier action of subject.7. Irritated : past
participle, used to express an earlier action 8. Transferred
: past participle, qualifies noun: collector.9.Arriving:
present participle,
qualifies noun: train. 10.Having finished: perfect
participle, used to express an earlier action. 11. Being
fine: present
participle, used to form absolute phrase.
12. Crying: present participle, used as object
complement of child. 13.
Killed: past participle, used as object complement of lion.
14. Seizing: present participle, used to qualify noun
people. 15. Taking: present participle, used to express an
action of the subject
Exercise2
1.Starting in the morning, we
arrived at midnight. 2. We met a boy carrying a heavy bag.
3. Taking pity upon him, I gave him some money. 4. Decorated
with lights, the house looked beautiful. 5. Seeing the
policeman, the robbers
ran away.6. The answer
being known to her, Monika put up her hand. 7. Finding the
door open, I went inside. 8. The police saw the body
floating down the river. 9. While reading the paper, he ate
his breakfast. 10. Having felt hungry, he went on eating.
11. Having reached home, they went to bed immediately. 12.
Having won a lottery, he bought a car.
Exercise3
1.Mr. Sale being the
only candidate,I appointed him to the post. 2. While sitting
on the grass, he was bitten by a snake. 3. It being a very
cold day, I remained in bed.4. Meeting me in the club, my
friend told me everything. 5. Going up the hill, they saw an
old grave. 6. Observing that the canal was rising, a gang of
labourers was sent for. 7. On hearing that there was a
vacancy, an application was sent by me. 8. On joining the
post immediately he was rewarded by them.
Chapter 16 THE VERB
: FINITE AND INFINITE
Exercise 1
1.
To
see, qualifies the verb :have come 2. To drink,
qualifies the noun : water 3. To live, qualifies the verb:
eat.4. To read, used as subject of the sentence. 5. To play,
used as object of the word
‘like’. 6. To err, qualifies the adjective human. 7.
To learn, qualifies
the adjective anxious. 8. Sing, qualifies the verb heard. 9.
To advice, qualifies the adjective easy. 10. To help,
qualifies the adjective willing. 11. To tell the truth,
qualifies the sentence. 12. To win, qualifies the verb wish.
13. To sit, qualifies the noun chair. 14. To accept,
qualifies adjective honest. 15. To be, qualifies the verb
appears. 16. To
obey, object of the preposition
But. 17. To eat, qualifies something. 18. Learn,
qualifies the verb helped. 19. To leave, object of
preposition About. 20. To go, qualifies the verb : was told.
Exercise 2
1.
They worked hard to
learn. 2. He was sensible enough to do the right thing. 3.
The problem is too difficult for the students to solve. 4.
The is too long to be finished today. 5. The school appoints
Rex to teach Geography. 6. We go to cinema hall to see a
movie. 7. To tell it frankly, I have no interest in
business. 8. These men held a meeting to select a manager
for the factory. 9. The man
took out a pistol to frighten all of us. 10. To
collect the old stamps is Pamela’s hobby.
CHAPTER 20 TENSES AND THEIR USES
Exercise2
1.ordered,
felt 2. Wondered, had done, had lent 3.did, could,
was 4. Could not cook, had 5. Had done,
did not
deserve 6. Ran , was
7. Inferred, said, was 8. Was, was 9. Took, was 10. Felt,
saw 11.
Could, would 12. Came, began 13. Ate , rang 14. Rode , saw,
were 15. Behaved, talked, remained, thought, kept, tried.
Exercise3
1.bind, hold 2. Chooses, finds
3.dreams,attempts 4. Knows, cannot 5. Guard,may 6. Gives,
may 7. Comes, has 8. Bellow, finds, are
9.promises,will be, expresses 10.talks,has 11.heard
12.will, can 13. Gives 14. Calls, finds, has gone 15. Is
washed,flock,can
Exercise4
1.
Has gained 2.carried
out 3.are waiting 4. Placed 5.was lying 6. Went 7.repaired
8. Lay 9.had gone 10. Lay,flowed
Exercise5
1.
Left 2.
Matriculated3. Was 4. Made 5. Came 6. Has gone 7. Sat 8. Had
been 9. Had reached 10. Did not 11. Do
12.frizen
CHAPTER26 WORDS FOLLOWED BY PARTICULAR
PREPOSITIONS
Exercise1
(a)1.of 2. In
3. to 4.
to
5.on 6. With 7. To 8. With
9. With 10. For
(b)1.of,with 2. Of 3.from,to 4. In, of 5.
Of 6. In 7. Out 8. Of 9. Of 10.with
(c)1. for 2. Of, at , in 3. With 4. For
5. To, for 6. With, over 7. To 8. To 9. In 10.with
(d)1. with 2. For 3. To 4. To 5. In 6. Of
7. Of 8. For 9. On 10. To
(e)1.in 2. For 3. To 4. Of 5. On 6. To 7.
On 8. Amongst/with 9.at 10. For
Exercise2
(a)1.for
2. On 3. For,to 4. To, of 5. Over
(b)1.by 2.to 3. About 4. Of, against 5.
With,of
(c)1.to,of,in 2. Of, about 3. For 4. Into
5. By
(d)1.to 2. To 3. By/from 4. To 5. To 6.
Into 7. To 8. From 9. For 10. With
Exercise3
(a)1.with,out to ,to , of (b)with, of, to
,up (c)of, to, with, of, at, of, in (d)to, to,on,
Exercise4
(a)1.on,into 2. Before, in from 3.
Besides 4.with 5. At, in 6. Between 7. Among
(b)1.since 2. From, till 3.for 4. By
Exercise5
1.about, of 2. Over, about 3. For 4. To
5. Of 6. At/about, with 7. To, by, to 8. Under,to 9. To 10.
With 11. To with, about/on, for, to 12. To, of 13. For, with
14. To 15. To, in 16. By, of
17. For 18.
With, to, in 19. For,for,of,of 20. About, of
CHAPTER27 THE CONJUNCTION
Exercise1
I.1.and: co-ordinating conjunction 2.
Before: subordinating conjunction
3.and:co-ordinating,threrfore:co-ordinating conjunction 4.
Unless: subordinating 5. Neither…….nor: co-ordinating
conjunction
II.(wrong words) 1.or 2.not only lost
3.when 4. Than 5. Like 6. Like 7. Does not invite 8. But,
yet 9. Until 10. Do not tell
Exercise2
1.
As 2.because 3.for
4.though 5.but 6.since 7.lest 8.so that 9.although 10.till
II.1.take care of yourself or you will
die.2.He deserted his brother as he was very proud. 3.You
must do as you are told otherwise you will be punished.
4.Though he tried to get up,he could not. 5. The policeman
ran after the thief but he could not catch him. 6. You may
not be successful , still, you ought to attempt the
question.7.All men were againstDr.
Johnson;nevertheless,hepersevered.8.He as well as you are
honest. 9. If you send me a message, I will come at once.
10. Lead me anywhere and I shall
go.
CLASS VIII, COMPUTER -
CH- 2 (SPREADSHEET –FORMULA)
1.
Tick the correct answer.
a.
Excel
b.
Cell
c.
Formula
d.
Cell Reference
e.
Comparison
f.
Relative
2.
True and False.
a.
True
b.
False(2/3)
c.
True
d.
False(+/=)
e.
True
f.
True
3.
Fill in the blanks.
a.
Spreadsheet
b.
Rows and Columns
c.
Labels, Values and Formulas
d.
Formula
e.
Parentheses()
f.
Autofill
g.
Constant
4.
Define the following.
a.
Cell Reference- Every cell in a worksheet has a unique address, called cell
reference. By default, cells are identified by a specific
column letter and row number.
b.
Cell Range- A group of selected or related cells in a worksheet is
called a cell range. Selected cells are highlighted on our
screen.
c.
Operator- A formula can contain one or more operators. An operator
specifies the type of calculation we want to perform.
5.
Answer in 1-2 sentences.
a.
How many rows and columns are there in a worksheet?
Ans: Excel
worksheet has 1048576 number of rows and 16384 columns.
b.
How do we switch between worksheets?
Ans: We can
switch to another worksheet in a workbook by clicking
worksheet tabs.
c.
What are the two different types of data present in Excel?
Ans:
Constants and Formulas are two different types of data
present in Excel.
d.
What are Operators?
Ans: A
formula can contain one or more operators. An operator
specifies the type of calculation we want to perform.
Examples- Arithmetic operators, Comparison operators etc.
e.
What do you mean by ‘Order of calculation’?
Ans: When a
formula contains more than one operator, Excel performs the
calculations in a specific order. We can use parentheses ()
to change the order in which Excel performs calculations.
6.
Answer Briefly.
a.
What do you mean by a spreadsheet program?
Ans:
Spreadsheet is a program that allows us to organize data,
complete calculations, represent data in graphs, and develop
reports. Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet program.
Excel allows us to organize data in rows and columns. These
rows and columns are collectively called a worksheet. A
spreadsheet file is called a workbook, which have many
individual worksheets. On each worksheet, data is organized
vertically in columns and horizontally in rows. Each
worksheet in Excel 2010 has 16384 columns and 1048576 rows.
b.
What is a formula? How is it useful in Excel?
Ans: A Formula is a sequence of values, cell references,
names of functions or operators (+,-,*,/, etc.) that
produces a new value from existing values. In other words,
formula is used to calculate numerical information and
display the resulting value in a cell. We can use formulas
to perform all kinds of calculations in our Excel data. For
examples, we can add the contents of a column of monthly
sales figures to calculate the totals sales.
c.
Defines the different types of operators with examples.
Ans:
A formula can contain one or more operators. An operator
specifies the type of calculation we want to perform. There
are different types of operators. These are
1.
Arithmetic Operators- we can use arithmetic
operators to perform mathematical calculations.
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
+
|
Addition
|
|
-
|
Subtraction
|
|
*
|
Multiplication
|
2.
Comparison Operators- We can use comparison
operators to compare two values. Comparison operators return
a value of TRUE or FALSE.
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
=
|
Equal to
|
|
>
|
Greater than
|
|
<
|
Less than
|
3.
Reference Operators-
The reference operators
combine two cell ranges to create a single joint reference.
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
:
|
Colon
|
|
|
Space
|
|
‘
|
Comma
|
d.
Differentiate between relative and absolute referencing.
Ans:
|
Relative referencing
|
Absolute Referencing
|
|
1.
The formula using the relative cell
reference adjusts the cell reference as it copies to
the destination area.
2.
Example- C5 is a relative cell reference.
|
1.
The formula using the absolute cell
reference keeps the cell reference constant
(absolute) in the formula as it copies it to the
destination area.
2.
Example- $C$5 is an absolute cell reference.
|
e.
What is Mixed referencing? Explain with example
Ans. A cell
reference with only one
dollar sign ($) before either the column or the row
is called a mixed cell reference. When it shows C$5, the
column reference changes when we copy this cell to another
column because it is relative. The row reference does not
change because it is absolute. When it shows $C5, the column
reference does not change because it is absolute. The row
reference changes when we copy this cell reference to
another row because it is relative.
English Language
Class 8
Book –A comprehensive
grammar of
current English Chapter 40
Transformation of sentences
Exercise 1
Part (a) and (b) are already done
Part c :
1.
As soon as he opened the letter
, he started the
weeping
.Or Hardly had he opened the letter when he started weeping.
2 As soon as he appeared on the stage , clapping started in
the hall. Or
Hardly had he
appeared on the stage when the clapping started in
the hall. 3 As soon as it was said , it was done. 4 As soon
as the captain ordered , the soldiers started firing. Or
Hardly had the Captain ordered when the soldiers started
firing. 5As soon as I reached home, it started raining. Or
Hardly had I
reached home
when it started raining.
[Changing patterns :No sooner + helping verb + subject +
main verb + object + than +subject + main verb + object . To
remove no sooner
we can write the sentence in two different forms i.e
to begin with as soon as or hardly …… when .These type of
sentences are the combinations of Principal clause and
Subordinate clause. In case of no sooner the part of the
sentence after ‘ than’ is called the principal clause
, the same way
in case of hardly
the part of sentence after ‘when’ is called the principal
clause and same in case of as soon as after comma . so
this part never changes in any form of
the sentence . the change occurs only in subordinate
clause i.e before than when or comma. We do not add any
helping verb just after
‘as soon as ‘
that we do while starting the sentence with no sooner
or hardly.]
Exercise 2. Change the degree of comparison
1 An ass is not as
intelligent as a horse.(When comparison is between two
things persons places etc the sentence can be written either
in positive degree or comparative degree.)2 A foolish friend
is not as good as a wise enemy.3 (a) No other sea port in
India is as good as
Mumbai.(B) Mumbai is better than all other sea ports
in India.[As the comparison of Mumbai is with all other sea
ports therefore it can be written in all the three degrees
.]4 Disraeli was greater than all other statesmen in
England.(b) No other statesman in England was as great
as Disraeli.5 Hoshiarpur id more fertile than most
other districts
.(b) Hoshiarpur is one of the most fertile districts.[As few
districts are equally fertile as Hoshiarpur
therefore it can also be written as in all the three
degrees by using ‘most other ‘ districts
in comparative and ‘one of the’ most fertile
districts in superlative degree ]6 Ther are few poets as
great as Kalidasa . (b) Kalidasa is greater than most other
poets. Dickens’ ‘David Copperfield’ is more popular than
most other books .(b)Dickens’ ‘David Cooperfield’ is one of
the most popular books . 8 Gold is more precious than most
other metals .(b) Very few
metals are as precious as gold. 9 To act is not as as
easy as to speak. 10 A motor car does not run as fast as the
bullet train. 11 I do not know
you as well as he does . 12He does not know me as
well as he does you. 13 No other man is as mean as he is
.(b) He is meaner than all other man . 14Let us see who runs
faster than all
others . 15 Nobody else does his work as honestly as he
does.
(b)He does his work most honestly.16 Macaulay writes more
graphically than most other historians. (b)
Macaulay is one of the historians who write most
graphically. 17 Jack does not ball as fast as John. Ashoka
was nobler than most other Indian kings .(b) Very few Indian
kings were as noble as Ashoka.19 A dead lion is not as good
as a live ass.20 None of his companions seemed as cheerful
as Jim.(b) Jim seemed to be the most cheerful of all his
companions .
Exercise 3 Substitute the verb form for the words italicized
:(change of nouns to verbs)
(a)1The
sectary did not reply for a few days.2 He accepted
all that
we proposed.3His song did not amused
me.4This appears to be a sound proposal.5 I
believe he does not mean what he says.6 Keats loved
poetry .7This pencil costs one rupee.8 I will be
engaged at
four o’clock.9 I did
not intend to do it.10He did not hope to succeed
in his effort.11His request for money was refused.12The
Mayor was not invited.13That was not she meant.14
It did not appear to
be a village no longer.
(b)
Substituting the noun form :(Change of verbs to noun)
1He neglected the choice of a good seat for
himself.2The fairy has a resemblance to a flower.3We
can learn everything at ease.4 I did it as per your
desire.5 I
am sorry for the rudeness he showed to your father.6H
e has faith in his innocence . 7 Have you received
the approval of your father for your choice ?8 I have
no intension of staying here during the the vacation.
9 He has intelligence enough to see through the
game.10 He works with such patience and diligence
that he is sure to win the prize.11 I found to my great
astonishment that the village was no longer visible.12
The member
offered an apology to the chairman for his remarks.13
The villagers were given a warning about the flood.14
Christmas is a time for
merriment.15 A snake is a reptile its
ungratefulness .
(C)
Substituting the adjective form of words: (Change of adverbs
to adjectives )
1 It was fortunate that we were well armed to repel
the attack.2 Frances Bacon was remarkably
industrious and intelligent.3 He is
proud of his wealth.4 It is probable that the sub
committee is not going to meet today.5 To be healthy
is to be wealthy.6 It
is unusual that
he is such a fast runner.7 It was easy
for me to get the
job if I tried.8 He who shirks labour will not be
prosperous.9 King Lear was not courageous enough
to write to Cordelia.10 The children proved very
troublesome. 11 It is possible that there will be
a sandstorm today.12 I am sure that this was his
native village.13 One of the soldiers was very strong.14
Being poor made him a thoughtful boy . 15 It is
obvious that the minister will be re- elected.
Exercise -d
Substitute the adverb form of the words : ( Change of
adjectives to adverbs )
1The lawyer examined the documents very carefully.2
You behaved insolently
and impertinently.3 Regan spoke harshly
and severely.4 He hates his neighbour
particularly.5 Suddenly Hamlet appeared
on the scene .6 The accused did not do that injury intentionally.7
Lincoln acted courageously and patiently.8
They lived together in their place peacefully and
happily.9 The slaves were beaten mercilessly . 10
Had she loved him sincerely , he would not have given
her up.
11 Flowers grow
abundantly in the garden. 12 He applied himself to his
work so thoroughly that soon he won the admiration of
all.13 I kept quiet purposely .14 Let us depart
peacefully. 15 Certainly he is not going to
attempt the meeting.16 Burke repeated his speech eloquently.
8 class History – Chapter No.1. A Period of Transition
I.
Tick the correct answer:
1.
Who discovered America in CE 1492?
a) Eli Whitney
b) Christopher Columbus
c) Amerigo Vespucci
d) Fedinand Magellan
2.
Who invented the “Spinning Jenny”?
a) James Watt
b) George Stephenson
c) Hargreaves
d) Arkwright
3.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the
Renaissance?
a) Rationalism
b) Humanism
c) Putting-out system
d) Scientific Spirit
4.
When was the Steam Engine invented?
a) CE 1785
b) CE 1793
c) CE 1769
d) CE 1815
5.
What does the word ‘laissez Faire’ mean?
a) Rebirth
b) Sphere of influences
c) Let us alone
d) Voyages of discovery
Answers:-
1.
(b)
2.
(c)
3.
(c)
4.
(c)
5.
(c)
II.
Fill in the blanks:
1.
The Renaissance thinkers believed in the life in the
__________.
2.
The term Reformation refers to two major developments, the
________ and the _________.
3.
Vasco-da-Gama reached ___________ on the west coast of
India.
4.
The Industrial Revolution began in England in about ________
5.
In 1793, Eli Whitney invented a _____________
Answers.
1.
World
2.
Protestant, counter reformation
3.
Calicut
4.
CE 1750
5.
cottongin
III.
Match column A with Column B
1.
John Kay
a) Mule
2.
James Hargreaves
b) Cotton gin
3.
Arkwright
c) Power loom
4.
Samuel Crompton
d) Steam engine
5.
Cartwright
e) Water frame
6.
Whitney
f) Spinning Jenny
7.
James Watt
g) Flying Shuttle
Answers:-
1.
(g)
2.
(f)
3.
(e)
4.
(a)
5.
(c)
6.
(b)
7.
(d)
IV.
State whether the following statements are True or False
1.
The Renaissance and the Reformation alongwith new voyages
ushered in the Modern Age.
2.
The Industrial Revolution began in Germany.
3.
McAdam devised railway tracks.
4.
The Rise of capitalism and imperialism can be attributed to
the Industrial Revolution.
5.
The East India Company gradually became rulers from being
traders.
6.
Martin Luther led the Reformation Movement.
Answers:
1.
True
2.
False
3.
False
4.
True
5.
True
6.
True
V.
Answer the following questions briefly.
1.
How did the Renaissance, Reformation and the new
geographical discoveries lead to the Modern Age?
2.
Give reasons why the industrial Revolution first began in
England.
3.
4.
Discuss the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society,
economy and polity.
5.
What is imperialism? Discuss the factors which led to the
rise of imperialism.
6.
Describe the general impact of imperialism with special
reference to South Asia.
Answers:-
1.
on pg no 11
Chapter at a glance points of Reformation and Renaissance
2.
on page no 10,
Points to remember (Point no 3) full
3.
on page no 7 Impact of Industrial Revolution.
Star from (1) (The Industrial upto world wars)
(2) (The Industrial upto production)
4.
on page no 8, 9 (both)
Imperialism
Start from the upto colony (in blue color)
then causes of Rise Imperializing
only points 1, 2, 3 on page no 8 and 4, 7, 9 on page no 9
5.
page no 10
Ist column 2nd paragraph (the east- upto of
india)
3rd Paragraph (SriLanka – upto British)
2nd Column (fram upto empire)
VI.
Give Reasons.
1.
Most of the countries in South Asia became colonies of
Europe.
2.
New inventions and discoveries led to the Industrial
Revolution.
Answers:
1.
on page no 9
2nd coloumn >> Impact on south Asia
Most of the ____ upto ____ world.
Political instability
Lack of economic values
2.
on page no 4
2nd coumn >> The Industrial Revolution >> 3rd
Paragraph >> (after 1750 new inventions upto over the
world.)
Class 8
Biology -
Chapter-The nervous system
|
Exercise
A.Fill in the blanks
(a)Axon hillock
(b) neurotransmitter
(c) neuromuscular junction
(d) mixed
(e) cerebrum
(f) hindbrain
(g) cell body
(h) hypothalamus
(i) cranial
(j) reflex action
B. Choose the correct option
1.(d)
2.(c)
3.(d)
4.(d)
5.(a)
6.(b)
7.(b)
8.(a)
C. Match the following
1-f
2-h
3-i
4-g
5-d
6-a
7-b
8-j
9-c
10-e
D. Answer the following
1.Nervous and endocrine system control and
co-ordinate the various activities of the body.
2. Neurone is made up of a cyton, dendrites and an
axon.the dendrites carry messages towards the cyton
and the axon carries messages away from the
cyton.The junction of the axon of one neurone and
one or more dendrites of another is called a
synapse.
3. The sensory neurones carry messages from various
parts of the body to the central nervous system
while the motor neurones carry messages from the
central nervous system to the effector organs.
4. A synapse between a motor neurone and a muscle
fibre is called a neuromuscular junction.
5. Nerves are cable like structures made up of
bundles of axons. Is no was covered by a layer of
connective tissue and has several blood vessels
within it.
6. The three type of nerves are
(a)Sensory neurons
(b)Motor neurons
(c)Mixed neurons
7. The cerebral spinal fluid filled cavities within
the brain are called ventricles.
8.The midbrain connects the forebrain to the hind
brain and spinal cord,and controls eye adjustments.
9.peripheral nervous system consist of the nerves
which arise from the brain and spinal cord. It
comprises 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of
spinal nerves.the peripheral nervous system has two
components the somatic or voluntary nervous system
and autonomic or involuntary nervous system.
10. The sympathetic nervous system raises the level
of an organ's activity during stress or danger while
the parasympathetic nervous system decreases organ's
activity.
E.Explain in brief
1. An axon carries impulses away from the cyton.
When an impulse reaches the end of an axon,it
stimulates the release of certain chemicals called
neurotransmitters.The neurotransmitters diffuse
across a synapse to stimulate the dendrites of the
next neuron. The cyton of this neurone generates an
impulse in response to the neurotransmitters, which
is carried along its axon in the same manner.In this
way an impulse travel from one neuron to another.
2.FOREBRAIN
(a)Cerebrum--controls learning, speech, memory,
emotion, reasoning, voluntary activities, response
to pain and temperature, and the senses.
(b)Hypothalamus--control endocrine system and
emotions.
3.GREY MATTER
The the cell bodies of most of the neurones are
located in the upper layers of the cerebral
hemisphere giving these layers a great appearance so
the cell bodies are called green matter.
WHITE MATTER
The axons of these neurons form bundles that appear
white and are thus called white matter. White matter
is mostly found in the deeper parts of the cerebrum.
4. The parts of hindbrain and their functions are as
follows
1 Cerebellum:-coordinates body movement, posture and
balance, helps in learning new movements.
2 Pons:-conveys message from the fore brain to the
cerebellum, helps control sleep, breathing,
swallowing, bladder function, eye movement,facial
expressions.
3 Medulla oblongata:-it controls involuntary
actions.
5.Diagram is on page no.70 fig.5.7
Function:-The spinal cord relays messages to and
from the brain through nerves.
6. Reflex action is an autonomic response to
stimulus requiring swift action.
For example:-we instantly blink when strong light is
flashed in our eyes.
|
|
CLASS VIII, COMPUTER -
CH- 2 (SPREADSHEET –FORMULA)
1.
Tick the correct answer.
a.
Excel
b.
Cell
c.
Formula
d.
Cell Reference
e.
Comparison
f.
Relative
2.
True and False.
a.
True
b.
False(2/3)
c.
True
d.
False(+/=)
e.
True
f.
True
3.
Fill in the blanks.
a.
Spreadsheet
b.
Rows and Columns
c.
Labels, Values and Formulas
d.
Formula
e.
Parentheses()
f.
Autofill
g.
Constant
4.
Define the following.
a.
Cell Reference- Every cell in a worksheet has a unique address, called cell
reference. By default, cells are identified by a specific
column letter and row number.
b.
Cell Range- A group of selected or related cells in a worksheet is
called a cell range. Selected cells are highlighted on our
screen.
c.
Operator- A formula can contain one or more operators. An operator
specifies the type of calculation we want to perform.
5.
Answer in 1-2 sentences.
a.
How many rows and columns are there in a worksheet?
Ans: Excel
worksheet has 1048576 number of rows and 16384 columns.
b.
How do we switch between worksheets?
Ans: We can
switch to another worksheet in a workbook by clicking
worksheet tabs.
c.
What are the two different types of data present in Excel?
Ans:
Constants and Formulas are two different types of data
present in Excel.
d.
What are Operators?
Ans: A
formula can contain one or more operators. An operator
specifies the type of calculation we want to perform.
Examples- Arithmetic operators, Comparison operators etc.
e.
What do you mean by ‘Order of calculation’?
Ans: When a
formula contains more than one operator, Excel performs the
calculations in a specific order. We can use parentheses ()
to change the order in which Excel performs calculations.
6.
Answer Briefly.
a.
What do you mean by a spreadsheet program?
Ans:
Spreadsheet is a program that allows us to organize data,
complete calculations, represent data in graphs, and develop
reports. Microsoft Excel is a powerful spreadsheet program.
Excel allows us to organize data in rows and columns. These
rows and columns are collectively called a worksheet. A
spreadsheet file is called a workbook, which have many
individual worksheets. On each worksheet, data is organized
vertically in columns and horizontally in rows. Each
worksheet in Excel 2010 has 16384 columns and 1048576 rows.
b.
What is a formula? How is it useful in Excel?
Ans: A Formula is a sequence of values, cell references,
names of functions or operators (+,-,*,/, etc.) that
produces a new value from existing values. In other words,
formula is used to calculate numerical information and
display the resulting value in a cell. We can use formulas
to perform all kinds of calculations in our Excel data. For
examples, we can add the contents of a column of monthly
sales figures to calculate the totals sales.
c.
Defines the different types of operators with examples.
Ans:
A formula can contain one or more operators. An operator
specifies the type of calculation we want to perform. There
are different types of operators. These are
1.
Arithmetic Operators- we can use arithmetic
operators to perform mathematical calculations.
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
+
|
Addition
|
|
-
|
Subtraction
|
|
*
|
Multiplication
|
2.
Comparison Operators- We can use comparison
operators to compare two values. Comparison operators return
a value of TRUE or FALSE.
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
=
|
Equal to
|
|
>
|
Greater than
|
|
<
|
Less than
|
3.
Reference Operators-
The reference operators
combine two cell ranges to create a single joint reference.
|
Operator
|
Description
|
|
:
|
Colon
|
|
|
Space
|
|
‘
|
Comma
|
d.
Differentiate between relative and absolute referencing.
Ans:
|
Relative referencing
|
Absolute Referencing
|
|
1.
The formula using the relative cell
reference adjusts the cell reference as it copies to
the destination area.
2.
Example- C5 is a relative cell reference.
|
1.
The formula using the absolute cell
reference keeps the cell reference constant
(absolute) in the formula as it copies it to the
destination area.
2.
Example- $C$5 is an absolute cell reference.
|
e.
What is Mixed referencing? Explain with example
Ans. A cell
reference with only one
dollar sign ($) before either the column or the row
is called a mixed cell reference. When it shows C$5, the
column reference changes when we copy this cell to another
column because it is relative. The row reference does not
change because it is absolute. When it shows $C5, the column
reference does not change because it is absolute. The row
reference changes when we copy this cell reference to
another row because it is relative.
English Language
Class 8
Book –A comprehensive
grammar of
current English Chapter 40
Transformation of sentences
Exercise 1
Part (a) and (b) are already done
Part c :
1.
As soon as he opened the letter
, he started the
weeping
.Or Hardly had he opened the letter when he started weeping.
2 As soon as he appeared on the stage , clapping started in
the hall. Or
Hardly had he
appeared on the stage when the clapping started in
the hall. 3 As soon as it was said , it was done. 4 As soon
as the captain ordered , the soldiers started firing. Or
Hardly had the Captain ordered when the soldiers started
firing. 5As soon as I reached home, it started raining. Or
Hardly had I
reached home
when it started raining.
[Changing patterns :No sooner + helping verb + subject +
main verb + object + than +subject + main verb + object . To
remove no sooner
we can write the sentence in two different forms i.e
to begin with as soon as or hardly …… when .These type of
sentences are the combinations of Principal clause and
Subordinate clause. In case of no sooner the part of the
sentence after ‘ than’ is called the principal clause
, the same way
in case of hardly
the part of sentence after ‘when’ is called the principal
clause and same in case of as soon as after comma . so
this part never changes in any form of
the sentence . the change occurs only in subordinate
clause i.e before than when or comma. We do not add any
helping verb just after
‘as soon as ‘
that we do while starting the sentence with no sooner
or hardly.]
Exercise 2. Change the degree of comparison
1 An ass is not as
intelligent as a horse.(When comparison is between two
things persons places etc the sentence can be written either
in positive degree or comparative degree.)2 A foolish friend
is not as good as a wise enemy.3 (a) No other sea port in
India is as good as
Mumbai.(B) Mumbai is better than all other sea ports
in India.[As the comparison of Mumbai is with all other sea
ports therefore it can be written in all the three degrees
.]4 Disraeli was greater than all other statesmen in
England.(b) No other statesman in England was as great
as Disraeli.5 Hoshiarpur id more fertile than most
other districts
.(b) Hoshiarpur is one of the most fertile districts.[As few
districts are equally fertile as Hoshiarpur
therefore it can also be written as in all the three
degrees by using ‘most other ‘ districts
in comparative and ‘one of the’ most fertile
districts in superlative degree ]6 Ther are few poets as
great as Kalidasa . (b) Kalidasa is greater than most other
poets. Dickens’ ‘David Copperfield’ is more popular than
most other books .(b)Dickens’ ‘David Cooperfield’ is one of
the most popular books . 8 Gold is more precious than most
other metals .(b) Very few
metals are as precious as gold. 9 To act is not as as
easy as to speak. 10 A motor car does not run as fast as the
bullet train. 11 I do not know
you as well as he does . 12He does not know me as
well as he does you. 13 No other man is as mean as he is
.(b) He is meaner than all other man . 14Let us see who runs
faster than all
others . 15 Nobody else does his work as honestly as he
does.
(b)He does his work most honestly.16 Macaulay writes more
graphically than most other historians. (b)
Macaulay is one of the historians who write most
graphically. 17 Jack does not ball as fast as John. Ashoka
was nobler than most other Indian kings .(b) Very few Indian
kings were as noble as Ashoka.19 A dead lion is not as good
as a live ass.20 None of his companions seemed as cheerful
as Jim.(b) Jim seemed to be the most cheerful of all his
companions .
Exercise 3 Substitute the verb form for the words italicized
:(change of nouns to verbs)
(a)1The
sectary did not reply for a few days.2 He accepted
all that
we proposed.3His song did not amused
me.4This appears to be a sound proposal.5 I
believe he does not mean what he says.6 Keats loved
poetry .7This pencil costs one rupee.8 I will be
engaged at
four o’clock.9 I did
not intend to do it.10He did not hope to succeed
in his effort.11His request for money was refused.12The
Mayor was not invited.13That was not she meant.14
It did not appear to
be a village no longer.
(b)
Substituting the noun form :(Change of verbs to noun)
1He neglected the choice of a good seat for
himself.2The fairy has a resemblance to a flower.3We
can learn everything at ease.4 I did it as per your
desire.5 I
am sorry for the rudeness he showed to your father.6H
e has faith in his innocence . 7 Have you received
the approval of your father for your choice ?8 I have
no intension of staying here during the the vacation.
9 He has intelligence enough to see through the
game.10 He works with such patience and diligence
that he is sure to win the prize.11 I found to my great
astonishment that the village was no longer visible.12
The member
offered an apology to the chairman for his remarks.13
The villagers were given a warning about the flood.14
Christmas is a time for
merriment.15 A snake is a reptile its
ungratefulness .
(C)
Substituting the adjective form of words: (Change of adverbs
to adjectives )
1 It was fortunate that we were well armed to repel
the attack.2 Frances Bacon was remarkably
industrious and intelligent.3 He is
proud of his wealth.4 It is probable that the sub
committee is not going to meet today.5 To be healthy
is to be wealthy.6 It
is unusual that
he is such a fast runner.7 It was easy
for me to get the
job if I tried.8 He who shirks labour will not be
prosperous.9 King Lear was not courageous enough
to write to Cordelia.10 The children proved very
troublesome. 11 It is possible that there will be
a sandstorm today.12 I am sure that this was his
native village.13 One of the soldiers was very strong.14
Being poor made him a thoughtful boy . 15 It is
obvious that the minister will be re- elected.
Exercise -d
Substitute the adverb form of the words : ( Change of
adjectives to adverbs )
1The lawyer examined the documents very carefully.2
You behaved insolently
and impertinently.3 Regan spoke harshly
and severely.4 He hates his neighbour
particularly.5 Suddenly Hamlet appeared
on the scene .6 The accused did not do that injury intentionally.7
Lincoln acted courageously and patiently.8
They lived together in their place peacefully and
happily.9 The slaves were beaten mercilessly . 10
Had she loved him sincerely , he would not have given
her up.
11 Flowers grow
abundantly in the garden. 12 He applied himself to his
work so thoroughly that soon he won the admiration of
all.13 I kept quiet purposely .14 Let us depart
peacefully. 15 Certainly he is not going to
attempt the meeting.16 Burke repeated his speech eloquently.
8 class History – Chapter No.1. A Period of Transition
I.
Tick the correct answer:
1.
Who discovered America in CE 1492?
a) Eli Whitney
b) Christopher Columbus
c) Amerigo Vespucci
d) Fedinand Magellan
2.
Who invented the “Spinning Jenny”?
a) James Watt
b) George Stephenson
c) Hargreaves
d) Arkwright
3.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the
Renaissance?
a) Rationalism
b) Humanism
c) Putting-out system
d) Scientific Spirit
4.
When was the Steam Engine invented?
a) CE 1785
b) CE 1793
c) CE 1769
d) CE 1815
5.
What does the word ‘laissez Faire’ mean?
a) Rebirth
b) Sphere of influences
c) Let us alone
d) Voyages of discovery
Answers:-
1.
(b)
2.
(c)
3.
(c)
4.
(c)
5.
(c)
II.
Fill in the blanks:
1.
The Renaissance thinkers believed in the life in the
__________.
2.
The term Reformation refers to two major developments, the
________ and the _________.
3.
Vasco-da-Gama reached ___________ on the west coast of
India.
4.
The Industrial Revolution began in England in about ________
5.
In 1793, Eli Whitney invented a _____________
Answers.
1.
World
2.
Protestant, counter reformation
3.
Calicut
4.
CE 1750
5.
cottongin
III.
Match column A with Column B
1.
John Kay
a) Mule
2.
James Hargreaves
b) Cotton gin
3.
Arkwright
c) Power loom
4.
Samuel Crompton
d) Steam engine
5.
Cartwright
e) Water frame
6.
Whitney
f) Spinning Jenny
7.
James Watt
g) Flying Shuttle
Answers:-
1.
(g)
2.
(f)
3.
(e)
4.
(a)
5.
(c)
6.
(b)
7.
(d)
IV.
State whether the following statements are True or False
1.
The Renaissance and the Reformation alongwith new voyages
ushered in the Modern Age.
2.
The Industrial Revolution began in Germany.
3.
McAdam devised railway tracks.
4.
The Rise of capitalism and imperialism can be attributed to
the Industrial Revolution.
5.
The East India Company gradually became rulers from being
traders.
6.
Martin Luther led the Reformation Movement.
Answers:
1.
True
2.
False
3.
False
4.
True
5.
True
6.
True
V.
Answer the following questions briefly.
1.
How did the Renaissance, Reformation and the new
geographical discoveries lead to the Modern Age?
2.
Give reasons why the industrial Revolution first began in
England.
3.
4.
Discuss the impact of the Industrial Revolution on society,
economy and polity.
5.
What is imperialism? Discuss the factors which led to the
rise of imperialism.
6.
Describe the general impact of imperialism with special
reference to South Asia.
Answers:-
1.
on pg no 11
Chapter at a glance points of Reformation and Renaissance
2.
on page no 10,
Points to remember (Point no 3) full
3.
on page no 7 Impact of Industrial Revolution.
Star from (1) (The Industrial upto world wars)
(2) (The Industrial upto production)
4.
on page no 8, 9 (both)
Imperialism
Start from the upto colony (in blue color)
then causes of Rise Imperializing
only points 1, 2, 3 on page no 8 and 4, 7, 9 on page no 9
5.
page no 10
Ist column 2nd paragraph (the east- upto of
india)
3rd Paragraph (SriLanka – upto British)
2nd Column (fram upto empire)
VI.
Give Reasons.
1.
Most of the countries in South Asia became colonies of
Europe.
2.
New inventions and discoveries led to the Industrial
Revolution.
Answers:
1.
on page no 9
2nd coloumn >> Impact on south Asia
Most of the ____ upto ____ world.
Political instability
Lack of economic values
2.
on page no 4
2nd coumn >> The Industrial Revolution >> 3rd
Paragraph >> (after 1750 new inventions upto over the
world.)
Class 8
Biology -
Chapter-The nervous system
|
Exercise
A.Fill in the blanks
(a)Axon hillock
(b) neurotransmitter
(c) neuromuscular junction
(d) mixed
(e) cerebrum
(f) hindbrain
(g) cell body
(h) hypothalamus
(i) cranial
(j) reflex action
B. Choose the correct option
1.(d)
2.(c)
3.(d)
4.(d)
5.(a)
6.(b)
7.(b)
8.(a)
C. Match the following
1-f
2-h
3-i
4-g
5-d
6-a
7-b
8-j
9-c
10-e
D. Answer the following
1.Nervous and endocrine system control and
co-ordinate the various activities of the body.
2. Neurone is made up of a cyton, dendrites and an
axon.the dendrites carry messages towards the cyton
and the axon carries messages away from the
cyton.The junction of the axon of one neurone and
one or more dendrites of another is called a
synapse.
3. The sensory neurones carry messages from various
parts of the body to the central nervous system
while the motor neurones carry messages from the
central nervous system to the effector organs.
4. A synapse between a motor neurone and a muscle
fibre is called a neuromuscular junction.
5. Nerves are cable like structures made up of
bundles of axons. Is no was covered by a layer of
connective tissue and has several blood vessels
within it.
6. The three type of nerves are
(a)Sensory neurons
(b)Motor neurons
(c)Mixed neurons
7. The cerebral spinal fluid filled cavities within
the brain are called ventricles.
8.The midbrain connects the forebrain to the hind
brain and spinal cord,and controls eye adjustments.
9.peripheral nervous system consist of the nerves
which arise from the brain and spinal cord. It
comprises 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of
spinal nerves.the peripheral nervous system has two
components the somatic or voluntary nervous system
and autonomic or involuntary nervous system.
10. The sympathetic nervous system raises the level
of an organ's activity during stress or danger while
the parasympathetic nervous system decreases organ's
activity.
E.Explain in brief
1. An axon carries impulses away from the cyton.
When an impulse reaches the end of an axon,it
stimulates the release of certain chemicals called
neurotransmitters.The neurotransmitters diffuse
across a synapse to stimulate the dendrites of the
next neuron. The cyton of this neurone generates an
impulse in response to the neurotransmitters, which
is carried along its axon in the same manner.In this
way an impulse travel from one neuron to another.
2.FOREBRAIN
(a)Cerebrum--controls learning, speech, memory,
emotion, reasoning, voluntary activities, response
to pain and temperature, and the senses.
(b)Hypothalamus--control endocrine system and
emotions.
3.GREY MATTER
The the cell bodies of most of the neurones are
located in the upper layers of the cerebral
hemisphere giving these layers a great appearance so
the cell bodies are called green matter.
WHITE MATTER
The axons of these neurons form bundles that appear
white and are thus called white matter. White matter
is mostly found in the deeper parts of the cerebrum.
4. The parts of hindbrain and their functions are as
follows
1 Cerebellum:-coordinates body movement, posture and
balance, helps in learning new movements.
2 Pons:-conveys message from the fore brain to the
cerebellum, helps control sleep, breathing,
swallowing, bladder function, eye movement,facial
expressions.
3 Medulla oblongata:-it controls involuntary
actions.
5.Diagram is on page no.70 fig.5.7
Function:-The spinal cord relays messages to and
from the brain through nerves.
6. Reflex action is an autonomic response to
stimulus requiring swift action.
For example:-we instantly blink when strong light is
flashed in our eyes.
|
|
|

