|
Class 6 Physics
G:
Give Reasons:
1.Ans:
Light can travel through the space because light do
not require any medium to travel.
2. Ans:
We can not see light through a bent rubber tube
because light
travels in a straight line.
3. Ans:
Shadow formed behind the opaque object
because
the opaque object do not let the light to pass through them.
H:
Differentiate Between the following:
1. Ans:
Umbra: The central dark region of the shadow
where no light reaches at all called Umbera.
Penumbra: The partial dark region around the
umbra
where some light reaches is called penumbra.
2. Ans:
|
Pinhole camera image
|
Shadow
|
|
1.
The colour of the
image is same as the colour of the object.
|
1.
The shadow of the
object is always black.
|
|
2.
The size of the
image is always smaller than the object.
|
2. The shadow of the
object
may be larger or smaller
than the object
|
3. Ans:
|
Solar eclipse
|
Lunar eclipse
|
|
1. When the moon comes in
between the earth and the
sun the solar eclipse
formed.
|
1. When the
earth comes in
between the sun and the
moon the lunar eclipse
formed.
|
|
2.
Moon castes its shadow on
earth.
|
2. Earth castes its
shadows on
the moon.
|
I. Short
Answer questions:
1. Ans:
one of the Properties of light is that it always travels in
straight line.
___________________________________________________
2. Ans:
Applications of rectilinear propagation of light:
1. Sun rays reaches to the earth.
2. Image formed in a pinhole camera
3. Shadow formation
___________________________________________________
3. Ans:
Characteristics of the image formed by the pinhole
Camera:
1. Image formed having same colour as the colour of
the object.
2. Size of the image is always smaller than the size
of
object.
___________________________________________________
4. Ans:
Shadow formed when opaque object is put in the path
of light called principal of shadow formation.
5.
Ans: Three things essential for shadow formation are:
1. Opaque object
2. Source of light
3. Screen on which shadow formed
___________________________________________________
6. Ans:
Two regions of shadow formation are:
1. Darke region called Umbera
2. Partially dark region called Penumbra
7. Ans:
(a)Natural pinhole camera: Small patches of
sunlight
through the leaves of plant on the ground.
(b) Shadow: Solar and lunar
eclipses
8. Ans:
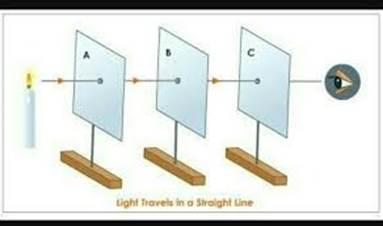
Take
three identical cardboards and label them as A, B, C. Make
holes at the centre of each cardboard. Fix the cardboards in
a straight line with the help of clay. Take a burning candle
and put it near the hole of cardboard A. Try to see the
burning candle through the hole of cardboard C. You will be
able to see the burning candle. Now place the cardboard B in
such a way that all cardboards are not in the straight line.
Now again try to see the candle light, this time you will
not be able to see the candle light. This activity shows
that light travels in a straight line.
Dig.:
9. Ans:
Working of a pinhole camera
Place a luminous object such as a burning wick (XY) of the
candle in front
of the pinhole, an inverted picture X’Y’ of the wick is
obtained on the wax paper. This picture is called the image.
The image obtained is inverted.
Such an image is formed because the light travels in a
straight path. Hence, light from the upper point X of the
wick passes through the pinhole and strikes the wax paper at
X’.
Similarly, light from the lower point Y of the wick
passes through the pinhole and strikes the wax paper (or
screen) at Y'.
When light from all other points between X and Y passes
through the pinhole they strike the wax between X' and Y'.
Hence, an inverted image is formed on the wax paper.

10. Ans:
Diagram from the book.
11.
Ans: Diagrams from the book.
12. Ans:
Lunar eclipse occur when earth comes in between the sun and
the moon. The shadow of earth falls on the moon. Lunar
eclipse can full or partial.
___________________________________________________
Class 6 Mathematics Ch 4
Exercise 4.1
Q1) 7×(15+5)
= 7×20
= 140
Q2) 6+3of7-5
= 6+3×7-5
= 6+21-5
= 27-5
= 22
Q3) 20+21÷3×2
= 20+7×2
= 20+14
= 34
Q4) 17+(8-5)×5
= 17+3×5
= 17+15
= 32
Q5) 25-48÷6+12×2
= 25-8+12×2
= 25-8+24
= 49-8
= 41
Q6) 7+(6×5+3)
= 7+(30+3)
= 7+33
= 40
Q7) 3+6÷3×2
= 3+2×2
= 3+4
= 7
Q8) 5×3-12÷4+8
= 5×3-3+8
= 15-3+8
= 23-3
= 20
Q9) 5×4-2×3+16÷4
= 5×4-2×3+4
= 20-6+4
= 24-6
= 18
Q10) 30-(5×2-15)
= 30-(10-15)
= 30-(-5)
= 30+5
= 35
Q11) 6-{5×3-(4-3)×16÷(-4)}
= 6-{5×3-1×16÷(-4)}
= 6-{5×3-1×(-4)}
= 6-{5×3+4}
= 6-{15+4}
= 6-19
= -13
Q12) [12÷(3of2-3)-9(5-4) ]
= [12÷(3×2-3)-9×1]
= [12÷(6-3)-9]
= [12÷3-9]
= [4-9]
= -5
Exercise 4.3
Q2 to Q7 is in the syllabus and already done in the class.
Exercise 4.4
Only Q3 is in the syllabus and will be done later in the
class.
Class – 6
Class – 6
Chapter 3 (
English Novel)
The whip
Comprehension
A Fill ups
1.
Trust
2.
Mud
3.
Wheels
4.
Living
5.
Vicar
6.
Railway
What do you think
1.
John began to teach Joe more and more about horses . Joe
worked hard and learned quickly. John began to trust Joe .
He allowed Joe to take a letter to a gentleman’s house and
ride Black beauty.
2.
Yes , Joe is right to
go and talk to Mr clay about the cruel cart driver . The
cart driver was hitting the horses hard with the whip. Sweat
was dripping from their legs and sides . They were not able
to pull the heavy cart out of the mud.
I would also have done the same thing.
3.
They all felt very sad .
Once I had also faced the
same situation . We had constructed a new house in the city
and I and my family had to shift there for our good
education . But it was very sad and painful to leave the old
place where I had so many friends and loving neighbours.
Language practice
1.
1 ans. Knocked
2. Began
3. Dropped
4. Shook
5. Move
2.
1. Hits
2. Wishes
3. Bricks
4. Mud
5. Sure
Guess the meaning
1.
Fashion – Style of dressing
2.
Proud – Self pride, arrogant
3.
Unfriendly – not polite
4.
Bad temper – impatient, often angry
5.
Rows – to fight
6.
Landed -to arrive
7.
Lonely – unhappy
8.
Ruined – to damage
Class -6
Chapter -5
(English
literature)
India at play
Comprehension
A . Match the
following.
1.Kith-Kith – Escargot
2.Chaturanga - Chess
3.Bhima – Wrestler
4.Independence day – kite flying
5.Dandi Biyo – Gilli danda
B. Complete these sentences
1 ans. Dangals
2 ans. Holding the breath
3 ans. Gilli danda
C. Answer these questions.
1 ans. In ancient times
it was played on raths or chariots and so was known
as the rathera.
2 ans. Abhimanyu the character of mahabharata is the
inspiration behind the game of kabaddi .
Abhimanyu got trapped in a chakravyuh created by his
enemies. In the same way Kabaddi is a game were a player
raids the opposing team tries
to touch an opponent and returns to his team.
3 ans. Celebration of Makar Sankranti and independence
day.
4 ans. An Indian king sent a chaturanga board to the king
of Persia from where the game spread to the rest of the
world .
D. Think and answer
1ans. The traditional games are a significant part of our
cultural heritage . We play them to exercise our body and
mind , to test our agility and skill and have fun . These
games also contain in them the spirit of our history . They
carry forward our legacy and give us our identity.
2 ans. Games have been a part of life in India since time
immemorial. Many games have originated in India and some are
being reinvented today . The pro kabaddi league has brought
kabaddi out of the shadows, while the IPL has doubled the
enthusiasm for cricket.
We rarely think of
games such as Kith – Kith (stapoo) , Gilli danda.
They are not much popular these days . These games do
not boast of having sports stars though they have been with
us for centuries.
Word study
E. Name of sports
1 ans. Gymnastics
2 ans. Basketball
3. Cricket
4. Badminton
5. Chess
6. Billiards
7. Tennis
8. Cards
F. Fill in the blanks
1. Summer sault
2. Stalement
3. Shuffle
4. Cues
5. Dunked
6. Ace
7. Shuttle
8. Crease
Grammar study
G .
1.Countable
2. Countable
3. Uncountable
4. Uncountable
5. Countable
6. Countable
7. Uncountable
8. Uncountable
H. Insert the or ×
1. the
,
the
2. ×
3. the , ×
4. ×
5. ×
6. the ,
the
7. ×
I cross word
Across
3. Dollop
6. Bar
7. Metre
Down
1.Bowl
2. Glass
4. Piece
5. Game
Class
6 English
WORKBOOK
Chapter 1
Ex A.
Answers
1.
The sky’s the limit
2.
Breathing fire
3.
Died laughing
4.
Sleeps like a log
5.
Go on forever
Ex. B
Match:
1.
By any means
2.
In writing
3.
Repeatedly
4.
Besides
Ex :C
|
Boy
|
Man
|
|
Glad
|
Angry
|
|
Cheerful
|
Annoyed
|
|
Joyful
|
Unhappy
|
|
Delighted
|
Distressed
|
Ex: D
1.
Article/adj.
2.
Verb/adj.
3.
Verb
4.
Noun
5.
Adverb
6.
Pronoun
7.
Adverb/adverb
8.
Prep.
9.
Prep.
10.
Pronoun
11.
Verb
12.
Adj.
13.
Conj.
14.
Adj.
15.
Adj.
16.
Noun
Fill ups
1
Heavy
2
Towards
3
Boy
4
Her
5
Beautifully
6
Drive/ride
7
Because
8
Near/at
9
Although
Chapter 2 (Malala)
Ex:A
Answers
1.
A ray of hope
2.
Clouded with
3.
Backbone
4.
Swollen headed
5.
Explodes
6.
Danced
7.
Twilight
8.
Shelved
Ex: B
Answers
Rhyming words: forbidden – hidden
Thrive – survive
Rhyming pattern:
a a b b
Grammar study:
Ex:C is your Homework.
Chapter 5 (India at play)
Ex:A
1.
Avid
2.
Keen
3.
Fervour
4.
Passionate
5.
Baffled
Ex:B
Match the following :
Answers
1.
C
2.
D
3.
B
4.
A
Ex:c
Answers
1.
–
2.
We should not listen to the music on high pitch.
3.
I eat the rice in a bowl.
4.
That track is not for car parking
5.
A volley of questions greeted her from all sides.
Ex:D
Answers
1.
C
2.
C
3.
U
4.
U
5.
U
6.
U
7.
C
8.
U
9.
C
10.
U
Ex:E
Answers
Fill ups
1.
Saplings
2.
Air
3.
Water
4.
Sugar
5.
Medals
6.
Players
Ex:F
Answers
Tick/wrong
1.
Tick
2.
Tick
3.
Tick /wrong
4.
Tick/Tick
5.
Wrong/wrong
6.
Tick/wrong
COMPUTER
CLASS
– 6
CH –
2 (COMPUTER LANGUAGES)
1.
Tick the correct answer.
a.
Program
b.
Machine language
c.
Assembly language
d.
BASIC
2.
True and False.
a.
False
b.
True
c.
False
d.
True
3.
Fill in the blanks.
a.
Machine
b.
Assembler
c.
Fifth
d.
Java
e.
Web
f.
HTML and Java
4.
Write the full form of the following.
a.
BASIC-
Beginners All Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code.
b.
PROLOG-
Programming Logic
c.
COBOL-
Common Business Oriented Language
d.
FORTRAN-
Formula Translation
5.
Answer in 1-2 sentences.
a.
What is a program?
Ans. A program is a set of instructions given to a computer
to get a particular task done.
b.
What is a computer language?
Ans. A computer language is a special language understood by
the computers. It consists of a set of words, symbols, and
codes that is used to write a computer program.
c.
Who are programmers and what is their work?
Ans. The people who can write programs are called
programmers. Their work is to develop codes for program.
d.
What do you mean by source program?
Ans. Source program is a program which must be translated
into machine language for the computer to understand it.
e.
What is the role of Assembler?
Ans. An Assembler is a program used to translate assembly
language into machine language so that the computer can
understand it.
f.
What is a language processor?
Ans. A language processor is a software that converts source
program into machine language because a computer does not
understand the program written in HLL or assembly language.
6.
Answer Briefly.
a.
How will you classify programming languages?
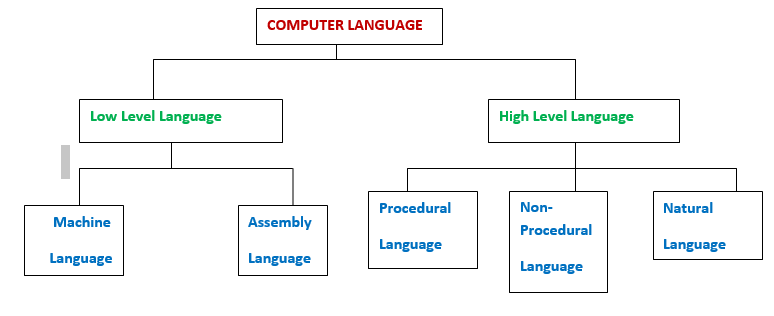
Ans.
Programming languages are classified into two major
categories:
1.
Low Level Language (LLL)
(i)
Machine Language (ii)
Assembly Language
2.
High Level Language (HLL)
(i)
Procedural Language
(ii)
Non-procedural
(iii)
Natural Language
b.
Differentiate between Procedural and Non-procedural
programming languages.
Ans.
Procedural Language-
A procedural language is also called a third-generation
language (3GL). In this language, the Programmer writes
instructions that tell the computer what to do and how to do
it.
Non-procedural language-
A non-procedural language is also called a fourth-generation
language (4GL). In this language, the programmer only
specifies what the program should do without explaining how.
c.
How is Machine Language different from Assembly Language?
Ans.
Machine Language-
A machine language, also called first-generation language,
is a language directly understood by a computer without any
translation. It refers to 0s and 1s that a computer can
understand as instructions.
Assembly Language-
Assembly language, also called second-generation language,
is also a low-level programming language. A program written
in assembly language uses short sequence of letters called
Mnemonic codes such as ADD for addition, MUL for
multiplying.
d.
Differentiate between compiler and interpreter.
Ans.
Compiler-
A compiler converts HLL program into machine language. It
converts the entire HLL program into machine language.
Interpreter-
Interpreter also converts HLL into machine language. It
converts one line of program at a time. It displays the
error one line at a time and goes to the next line only
after correction of that error.
CH –
4 (WORD PROCESSOR – TABULAR PRESENTATION)
1.
Tick the correct answer.
a.
Table
b.
AutoFormat
c.
Cell
d.
Left
e.
Macro
2.
True and False.
a.
True
b.
False
c.
False
d.
True
e.
True
3.
Fill in the blanks.
a.
Microsoft Word
b.
Alt+N+T+I and
Alt+N+T+D
c.
Dashed
d.
Split cells
e.
Triple-click
4.
Answer in 1-2 sentences.
a.
What is MS-Word?
Ans. Microsoft
Word is a full-featured word processing program. It allows
us to create and manipulate documents, containing text and
sometimes graphics.
b.
What is a Table?
Ans. Table is a way of organizing information into rows and
columns. We can easily re-arrange rows and columns or format
the content of a table.
c.
What do you mean by a cell?
Ans. Cell refers to the intersection of a row and a column
in the table. We can insert all types of data in cells,
including text and graphics.
d.
Why do we need to select cells?
Ans. We need to select table cells, rows and columns in a
table to perform editing tasks, and apply formatting to all
the selected areas of the table.
e.
Why do we combine cells in a table?
Ans. We can combine two or more cells in our table to create
one large cell. Combining cells is useful when we want to
display a title across the top or the down side of our
table.
f.
Write down the shortcut .keys to move the insertion point
from cell to cell in a table.
Ans. 1. Tab key
- To move to the next cell.
2.
Shift+Tab – To move to the previous cell.
3.
Arrow keys – To move one cell in the arrow’s
direction.
4.
Click on the cell in which we want to type.
5. Answer Briefly.
a. What are the
three ways to create a table in MS-Word?
Ans.
Creating a Table – 1. Click on the document
where we want to insert table.
2 Click on the
Insert tab.
3 Click on
Table button.
4 Drag mouse
pointer to select number of rows and columns in table.
Insert a Quick Table
- 1. Click on the document where we want to insert table.
2 Click on the
Insert tab.
3 Click on
Table button.
4 Click on
Quick Tables.
Draw a Table
- 1. Click on the document where we want to insert table.
2 Click on the
Insert tab.
3 Click on
Table button.
4 Click on Draw
Table.
b. What is the
purpose of aligning the text in a cell?
Ans. We can enhance the appearance of our table by changing
the position of the text in cells. Word tables alignment
options include the basic left, right, center and justify
alignments as well as vertical alignments. By default, Word
aligns our table text to the left inside each cell.
c. Why do we use
various table styles?
Ans. We can format our table by assigning the formatting
styles that are designed specifically for tables. Table
styles offer a variety of designs that includes shading and
coloring, borders and fonts, etc.
d.
How will you convert
tables to text?
Ans. 1. Save the
document .
2 Select the
table we want to convert. This activates the Table Tools
ribbon.
3 Click on
Layout tab, and on the
right end choose Convert to Text.
e.
Differentiate between splitting cell in a table and
splitting table.
Ans. Splitting
Cell in a Table – We can split one cell into two or
more cells in our table. We can even split cells into
columns and rows.
Splitting a Table
– We can split one table into two tables if we want to enter
a significant amount of information in one table.
Class 6 Chemistry Chapter
1
2Q.Define the following terms:
1Ans.organic chemistry-It deals with the study of
the structure, properties, composition, reactions and
preparation of carbon containing compounds which are present
mainly in living things.
2.central science- chemistry is sometimes called the
central science because it's so important to other
fields of science, like biology, geology, astronomy,
physics, medicine and engineering, etc.
3.Preservatives-Substances added to food to
slow down or prevent the growth of microorganisms .
3Q. Answer the following questions in short:
1Q. What is chemistry?
Ans. It is the branch of science which deals with
the study of substances, their structure, composition
and properties.
2Q. Name four items of daily____ knowledge of
chemistry.
Ans. 1.Medicines 2.Food 3.Cosmetics
4.Clothing.
3 Ans. Inorganic chemistry- It deals with the study
of the synthesis, structure and properties of compounds of
elements in non-living materials like rocks, soil, etc.
Organic chemistry-It deals with the study of the
structures and properties, composition, reactions, and
preparation of carbon containing compounds which are mainly
present in living things.
4 Ans.Bunsen burner is used to heat substances in a
laboratory.
5 Ans. Chemistry is called the central science
because it's so important to other fields of sciences, like
biology, geology,
astronomy, physics, medicine, engineering, etc.
4Q.Answer the following questions in details:
1Ans. Agriculture- chemistry has helped in various
ways by use of chemical compounds that are as follows:
Fertilisers-It is added to the soil
to improve the fertility of the soil. Examples:Urea,
potassium
Sulphate, etc.
Insecticides-It is used for killing insect that
infect and destroy
crops. Example:BHC, DDT, Nicotine, etc.
Fungicides-It is used for destroying fungi, which
destroy crops.
Example: copper sulphate Pentahydrate and
hexachlorobenzene.
Herbicides-It is used for killing weeds which grow
along with
the crops. Example:Glyphosate and Simazine.
2 Ans. The main five branches of Chemistry and their
scopes
are:
1.Analytical chemistry-It is art and science
of determining what matter is made of, it's percentage
composition and how much of it exists.
2.Biochemistry-It deals with the study of
chemical processes of living organisms.
3.Inorganic chemistry-It deals with the study
of the synthesis, reactions, structures and properties of
compound of elements.
4.Organic chemistry-It deals with the study of
structure, properties, composition, reactions and
preparation of carbon containing compounds.
5.Physical chemistry-It deals with the relations
between the physical properties of substances and their
chemical composition and transformation .
3Ans. 1.Follow all written and verbal instructions
carefully.
2.Never work alone in the laboratory.
3.Always wear a lab coat, goggles and gloves in the
laboratory.
4.Perform only those experiment given by your
teacher.
5.Never taste or inhale odorous chemical or solution
without the instructor's permission.
6. Keep your hands away from your face, eyes, mouth
and body while using chemicals or lab equipments.
4Ans1.Cosmetics-Cosmetics are substances or products
used to enhance or alter the appearance or fragrance of the
body.
2.Chemicals-Chemicals are also used to perform
various diagnostic tests such as blood tests, urine tests,
etc.
3.Medicines-Medicines like antiseptics and
disinfectants are used for curing the patients.
4.Food and agriculture-Contribution of chemistry has
helped agriculture in various ways by use of chemical
compounds that are fertilisers, insecticides, fungicides and
herbicides.
Most of the foods are also obtained through various
chemical processes, refined oils, butter,cheese,etc.Some
methods of food preservatives are canning, freezing,
pickling, etc.
5Ans.Alchemists believed they could refine base
metals such as iron into precious metals such as gold if
they could just find the mythical substance they called
Philosopher's stone.
The philosopher's stone they searched
for wasn't an actual rock. Instead, it was supposedly a
magical wax, liquid or powder that could heal ailments and
prolong life, as well as change base metals into
precious metals..
Think critically
1.State the functions of the following apparatus:
a. Beaker-It is used for holding or measuring small
quantities of liquids.
b. Measuring cylinder-It is used for measuring
volumes of liquids.
c. Retort-It is used in distillation experiment.
d. Flask- It is used to store or heat the liquid
substances.
e. Test tube-It is used to heat small quantities of
liquids or mix different liquids.
Diagram-based Question
1.Name the following apparatus and give one function
of each.
a. Conical flask.
It is used is used for mixing of different
solutions.
b. Beehive shelf.
It is used for collecting gases by the downward
displacement of water.
c. Wire gauze.
It helps to spread the flame uniformly.
d. Thistle funnel.
It is used to allow entry of reactant into a flask.
2.Complete the following flow chart.
Complete the flow chart from
Fig. 1.3 on page no-3.
Class 6th
English language
Chapter 7
Answers:
Ex A:
Choose the correct option.
1. Masculine gender
2. Both
B. Write
the opposite gender
Answers:
1.
Queen
2.
Peahen
3.
Duchess
4.
Horse
5.
Vixen
6.
Actress
7.
Priestess
8.
Bridegroom
9.
Milkmaid
10.
Widower
C. Rewrite the following sentence
Answers:
1. Prince
2. Bitch/cock
3. Actress
4. Headmistress
5. Tigress/lion/fox
6. Empress
7. Uncle
8. Inspector
9. Huntress /duck
10. Poetess/authoress
Ex D is the Homework for students.
Ex. E
1.
Vixen
2.
Niece
3.
Empress
4.
Sow
Ex. F is the
Homework for the students.
Chapter:
10
Ex.
A
Answers
1.
Third
2.
Emphatic pronoun
Ex. B
Answers
1.
Whose
2.
Who
3.
That
4.
Whom
5.
Which
Ex. C
1.
me
2.
something
3.
nothing
4.
anything
5.
me
Ex. D
1.
What
2.
Which
3.
Which
4.
What
5.
Whose
Ex. E
Join sentences using relative pronoun
1.
We met the sailors whose ship was wrecked.
2.
This is the man whose wife was killed in accident.
3.
The thief who stole my laptop has been arrested.
4.
I know the
brave boy whom the class teacher punished.
5.
The man who was killed in an accident was the father of a
friend of mine.
Ex. F
Fill with “self” form:
1.
itself
2.
yourself
3.
themselves
4.
yourself
5.
themselves
Ex G
Choose the correct pronoun
1.
herself
2.
him
3.
me
4.
us
5.
him/he/them
Ex. H
Pronoun
Kind
1.
himself Reflexive
2.
him
Personal
3
Me/Whom
Personal /
Relative
4
That
Relative
5
What/you
Interrogative/personal
Ex I : is your Homework.
Class
VI - Biology
- Chapter 1
Ex F-Give one important difference between the following
1.Parallel venation:
Veins are arranged in parallel rows to each other.e.g
Banana,grass
Reticulate venation:
Veins are irregularly distributed without a definite
pattern.e.g
Peepal,mango
2.simple leaf:
A simple leaf has single,undivided leaf blade.
E.g Chinarose
Compound leaf:
A compound leaf has a leaf blade that is divided into many
parts called leaflets.
E.g Rose
3.Tendrils:
Thin,wiry and spiral structures that help a plant to climb
by taking support are called tendrils.
Spines:
Thin and pointed structures used by the plants for defense
and to reduce transpiration are called spines.
ExG
Ans1-Photosynthesis occurs in a lamina of a leaf.
Ans2-Leaves are modified into spines in a cactus plant.
Ans3-The structure that helps a pea plant to climb is
tendrils.
Ans4-Pitcher plant is an insectivorous plant.In a pitcher
plant:
(a)Main pitcher is a modified leaf lamina.
(b)Lid is a modified leaf apex.
(c)Coiled part of pitcher is a modified petiole.
Ans5-China rose leaf is a simple leaf because the leaf blade
is undivided but rose leaf is a compound leaf as its leaf
blade is divided into many leaflets.
Ans6-Arrangements of veins in a leaf is called venation.
Ans7-E.g of parallel venation-banana,grass.
E.g of reticulate venation- peepal, mango.
Ans8-In a Bryophyllum leaf,buds appear along the margin of
the leaf that give rise to a new plant.
ExH- Hots:
Ans1If we cover the leaves of a plant with a polythene bag
and keep it in sunlight and water it regularly,we will
observe water droplets on the inner side of the polythene
bag due to transpiration by the leaves.
No,the leaves will not be able to carry out photosynthesis
as the leaves will not get the carbondioxide.
Ans2-Leaves wilt during the afternoon in bright sunlight
because the rate of transpiration is very high.Water is
needed to revive them
Note:fig 1.1,1.2,1.3,1.6,1.7 must be drawn in the classwork
copy.
Class 6 – History – chapter - 3
Chapter
3
I. Tick the correct answer
1. C
2. B
3. B
4. A
5. A
II. Fill ups
1. Pharaoh
2. Mummification
3. Pyramids
4. Wheat and bread
5. Agriculture
III. T/F
1. T
2. F
3. T
4. T
5. F
IV. Matching
4
1
2
3
V. Q/ As
1. What was the position of the king in the Egyptian
society?
Ans. The king had unlimited powers and was the political and
religious head of his people. He was called the Pharaoh. He
was considered to be God's representative on earth, and his
statues were installed in the temples. The people worshipped
him as a God.
2. Mention the contribution of ancient Egyptians in the
filed of astronomy?
Ans- the solar calender has been one of the greatest
achievements of the Egyptians. They observed that the star
Sirius appeared on the horizon when the floods reached Cairo
and this happened after every 365 days. It inspired them to
make the first known calendar of 365 days in a year of 12
months, each of 30 days.
3. Why is the Egyptian civilization called the gift of Nile?
Ans_ Without the river Nile , Egypt would have been a desert
. There is hardly any rainfall in Egypt . Egypt is therefore
called the “ Gift of Nile " .
4. Describe the important features of Egyptian art and
architecture.
Ans-- They developed the art of preserving the body to great
perfection a process called mummification.Pyramids, Sphinx
and temples at Karnak and Abu Simbel are the examples of
Egyptian architecture sculpture.
5. What do you mean by the term hieroglyphics?
Explain its features also.
Ans--- The Egyptians developed a kind of picture writing
known as hieroglyphic, which means holy writing.
Features
1.Pictures and signs represented their ideas. 2.It had about
500 signs. 3.The Egyptians used pens made of reed. Ink was
made of gum and soot.
Class 6 History civics – chapter 4
I. Tick the correct answer.
1. D
2. C
3. B
4. B
5. A
II. Fill ups
1. Urban
2. Sahiwal
3. Indus
4. Great granary
5. Bronze
6. Burnt
7.1500
III. Matching.
3
4
5
1
2
IV. Q/As
1. Who discovered the Indus valley civilization and when?
Ans- In 1921 an Indian archaeologist, Mr Daya Ram Sahni,
discovered the ruins of the city of Harappa. In 1922 Dr
Rakhal Das Bannerjee discovered the ruins of Mohenjodaro the
Larkana district of Sind.
2. Name the different sites of Indus valley civilization.
Ans- Lothal, Kalibangan, Banawali, Sutkagendor, Alamgirpur,
Dholavira.
3. Describe the town planning and drainage system of the
indus valley civilization.
Ans- Town planning:-
The cities of Harappa and i.Mohenjodaro were divided into
two parts, citadel and lower town.
ii.The smaller streets joined the main road at right angles.
iii.The streets had lamp-posts.
Drainage system:-
The street drains were covered with stone slabs or bricks
and had manholes at regular intervals.
4. Describe the great bath. where has it been found? What
was it used for?
Ans- the Great -Bath is a rectangular structure resembling
a swimming pool. It is example of beautiful brickwork. It
has been found at Mohenjodaro. It was used for religious
bathing.
5. Describe the religion of Indus valley civilization.
Ans- Religion:-
people worshipped Mother Goddess and Pashupati. They also
worshipped pipal tree and animals such as the humped bull.
6. Name three social classes of the indus valley
civilization.
Ans- The ruling class consisted of rich merchants and the
priests. They lived in the Citadel. The second class or
group was of small merchants, artisans and craftsmen. They
lived in the lower town. The labourers formed the third
group and lived in outer limits of the city.
7. What were the probable causes which could have brought
about an abrupt end to the indus valley civilization?
Ans- Decline of the Civilisation : destroyed by invaders •
natural calamities such as, earthquakes, floods, epidemic •
Indus might have changed its course.
V. Give reasons
a. Carried on trade with mesothelioma.
Ans- because trade was carried on from the port of Lothal.
Here big dockyard has been discovered.
b. Produced surplus grains.
Ans- because granaries were discovered at Mohenjodaro and
Harappa.
c. Had an idea of metallurgy.
Ans- because bronze figures of dancing girl and
bearded man were discovered.
Class 6 – Maths – chapter 11
Exercise 11.1
Q1)
1)True 2)False 3)False 4)True
5)False 6)True 7)True
Q2)
1)two 2)dot(.) 3)collinear points
4)parallel lines 5)length,breadth,thickness
6)definite 7)length
Q3)
1)collinear 2)not collinear 3)not
collinear 4)not
collinear 5)collinear
Q4)
1)Plane 2)Plane 3)Point
4)Line segment
5)Plane
Q5)
1)Infinite lines 2)Only one line
3)None
4)Only one line
Q6)
1)Intersecting lines
2)Parallel lines
3)Intersecting rays
4)Parallel lines
Exercise 11.2
Q1)1,2,4 are plane closed figures
Q2)
1)three 2)four,closed
3)rectangle
4)two 5)90
Q3)
1)greenboard,book
2)chess board,carrom board
3)plate,coin
Q4)
1)Crossing of railway track,scissors
2)railway track,ladder
3)grid paper,floor tiles
Q5)
1)True 2)True 3)True
4)True
5)False
Q6)Lines l and o are perpendicular to line AB.
Q7)
1)p and q , l and m
2)p and q perpendicular to l
p and q perpendicular to m
3)yes
Class
6 English Literature
Chapter
-2 Malala
Comprehension
A.
Answer these
questions.
1 ans.
Courage and kindness will always survive.
2 ans.
The lines mean that we realise the importance of light when
we see darkness . We also realise the importance of our
voices when we are silenced.
3 ans.
(a) Malala says these lines.
(b)
This shows that Malala was a brave girl . She raised her
voice because she knew the importance of education.
4 ans.
She started her blog to share her thoughts and educate
people how to fight for their rights . She started working
towards girl education in Muslim countries.
5 ans.
Malala is a known person all over the world . People liked
her powerful messages about injustice and the struggle to
overcome it.
B.
Answer. Malala spoke up for girls right to education , even
blogging about her experience living under the Muslim
conditions . She won Nobel Peace Prize . She believed in the
words “Believe in love . Make your heart beautiful.
Word
study
c.
|
Word
|
Literal meaning
|
Symbolic meaning
|
|
Light
|
Illumination
|
Hope, goodness
|
|
Spark
|
Flash of light
|
To kindle inspiration
|
|
Radiance
|
Glowing
|
Strength
|
|
Heart
|
An organ of body
|
Love, care
|
|
Voice
|
Sound
|
Feelings
|
|
Sky
|
Space around the earth
|
Height of success
|
D.
Rhyming Words
1.Forbidden – hidden
2. Thrive – survive
3. Heart – start
4. Consternation – education
5. Dreams – screams
6. Choice – voice
7. Cry – sky
Grammar study
E Tick the once
that are sentences
1 . The box of chalks near the board.
×
2. Ruma saw frogs in the pond.
√
3. The class room on the third floor.
×
4. Sasha smiles.
√
5. When will grandpa visit us.
√
6. My aunt who is a doctor.
×
7. Meet the librarian after school hours. √
8. The sun
rises.
×
F
1. a . Our teacher teach us science very nicely. (
statement)
b. What is the name of the teacher who teach you science? (
question)
c. Techer please teach us science
today.(request)
d. How nicely our teacher teach us science ! (Exclamation)
2. a. The children are planting the saplings. ( statement)
b. Did the children plant the saplings? (Question)
c. The children must plant the saplings. (command)
d. How nicely the children planted the saplings!
( exclamation)
3. a. We saw an interesting match. ( statement)
b. Did we saw an interesting match last month? ( question)
c. We must see the interesting match.
(Command)
d. What an interesting match we saw! ( exclamation)
G. Change into questions.
1. Did the teacher encourage me to do well?
2. Is Deepa Malik the first Indian woman to win a medal in
Paralympic Games?
3. Has Radhika gone to sleep?
4. Will your mother know the answer?
5.Has Sushil
read another story by Kenneth Graham?
H. Change into request.
1. Can you please pass me some salt.
2. Can you meet me in the conference room at 4:00 p.m..
3. Please talk softly in the hospital.
4. Could you please hold this parcel for me.
5. Please add some sugar to sweeten the curd.
Geography class 6 Chapter 2 Landforms
1.
Fill in the blanks
A)
Erosion
B)
Mount Everest
C)
Fold
D)
Block mountain
E)
Volcanic
2.Match the following
A)
3
b)
6
c)
7
d)
1
e)
2
f)
5
g)
4
3. write T
for true and F for false
a) T
b) F
c) F
d) F
g) T
4.choose the correct answers
a) 4
b) 2
c) 2
d) 3
e) 1
f) 2
5. Answer the following in brief
Ans.A. A natural feature of the Earth’s surface is
called Landforms. Mountains, plains,
valleys, plateaus, deserts and islands.
Ans.B. A mountain formed by natural faults in the
Earth’s crust are called block mountains.
Ans.C. Volcanic mountains are formed due to volcanic
erupations.eg—Mt Kilimanjaro in Africa.
Ans.D. A plateau is a type of landform that is a
raised area of land with a flat top.e.g.-The Deccan plateau
in India.
Ans.E. Volcanoes is an opening in the Earth’s crust
through which lava, volcanic ash and gases escape on the
earth surface, when the ash and lava cools it builds a cone
of rock called volcanic mountain.
Ans.F. Mountains are a storehouse of water because
many rivers originate from the glaciers which are formed in
mountains.
6.
Answer the following in detail
Ans (a) The different kinds of mountains in the world are :-
1.Fold Mountains – A mountain that is created when two of
Earth’s tectonic plates are pushed together.
2.Block Mountains- A mountain formed by natural faults in
the Earth’s crust.
3. Volcanic Mountains- Volcanic mountains are formed due to
volcanic eruptions.
Ans(b) The unique feature of Earth’s lithosphere is its
tectonic activity.This leads to the formation of various
landforms like mountains.most tectonic activity takes place
at the boundaries of these plates,where they may collide
tear apart or slide against each other.
Ans(c) 1.Fold Mountains – A mountain that is created when
two of Earth’s tectonic plates are pushed together.for
example :- The Himalayan Mountains,Alps,Aravali and the
Andes are formed by this process.
2.Block Mountains- A mountain formed by natural faults in
the Earth’s crust.Sierra Nevada mountain range in California
, The Rhine Valley and the Vosges Mountain in Europe are the
examples of Block Mountains.
3. Volcanic Mountains- Volcanic mountains are formed due to
volcanic eruptions.Mount Fuji in Japan and Mount Kilimanjaro
in Africa are examples of Mountains formed by volcanic
eruptipons.
Ans(d) Different kinds of Plateaus in the world are :-
1.
Tectonic Plateaus-continental blocks are reffered to as
tectonic plateaus ,it is further classified into (a)
Continental plateau (b) Intermontane plateau (c) Piedmont
plateau.
2.
Residual plateau-when old fold or block mountains get warm
down by million of years erosion they formed Residual
plateaus.
3.
Volcanic plateaus -these kinds of plateaus are formed by the
resistant lava caps that protect the land from erosion and
maintain its high elevation after the surrounding land has
been worn away.
Ans(e) Antarctica lies in the extreme end of the southern
hemisphere and it is extremely cold and covered with ice.
For this reason it is also called the Frozen continent and
people can not live permanently .
Ans(f)
Importance of
plains are :-
1
The terrain is ideal for habitation.
2
Transpotation is easier.
3
The soil is fertile with easy access to water.
4
Cultivation is easier as compared to mountain.
Ans(g) 1..Mountain and plateau
Mountain ----a mountain is a landform that rises above the
surrounding terrain. They are usually triangular in shape
.
Plateau------A plateau is a type of landform that is a
raised area of land with a flat top.It is also called
elevated flat-topped tableland.
G(2)-----plains and plateau
Plains ----Flat low-lying areas are known as plains Plains
have always been more preferred for habitation.
Plateau-----A plateau is a type of landform that is a raised
area of land with a flat top .it is also called elevated
flat-topped tableland.
G(3) -------young mountains and old mountains
Young mountain----------young mountains have pointed peaks
and they are very high ,the Himalayas in India and Alps in
Europe are the prominent examples.
Old mountains-----------old mountains have round peaks and
they are not very high,the Aravallis in India and Ural in
Europe are the examples of old mountains.
Ans (h)------River plans are densely populated than
mountainous region ,in India the Indo-Gangetic plains are
the most densely populated regions because the soil of the
plans is generally very fertile as it has rich deposits made
by the rivers. Cultivation is easier as compare to mountains
because there are no slopes. That’s why plans have always
been more preferred for habitation than mountains’ regions.
Class - 6
English Language
Chapter 1
The sentence
Ex 1
A.
Tick
the correct option
1.
A group of words that make up
complete sense is called a
sentence
2.
A sentence always begins with a
capital
letter
3.
A sentence ends with a
full stop
4.
We put a question mark at the end of an
interrogative sentence
5.
An imperative sentence expresses
command
6.
“What a great singer Tansen was!”
exclamatory
sentence
B.
Identity the kind of sentence in the following
1.
May I help you?
Interrogative
2.
Stop laughing.
Imperative
3.
My doctor told me to take rest.
Assertive
4.
Please let him go.
Imperative
5.
Anu, hand me your shirt.
Imperative
6.
How kind of you!
Exclamatory
7.
What a foolish man you are!
Exclamatory
8.
Have you solved the puzzle yet ?
Interrogative
9.
He stole my books.
Assertive
10.
Respect your teachers.
Imperative
C.
Learner’s Drill
Sentence Mix-up
Arrange the jumbled words
1.
The boy went to the shop.
2. He hit the tennis ball hard.
3. She went to play very early.
4. Take the dog for a walk.
5. Finish your homework and then go to bed.
6. They are going for shopping to buy new clothes
for school.
7. Are you going for movies today ?
8. They can go for school but they can’t go for
swimming.
Subject
and Predicate
Chapter 2
A.
Choose the correct option
Answers
1.
Subject
2.
Imperative
B.
Divide into subject and
predicate
Subject. Predicate
1.
Barking dogs
seldom bite.
2.
The little girl
is playing
with her toys.
3.
The girl wearing a pink frock
Is
my sister.
4.
The man standing in a corner
Is a doctor.
5.
A bad workman
blames his tools.
C.
Add predicates
Answers :
1.
Is a
good exercise..
2.
Is a
big city.
3.
In the
west.
4.
Is a
doctor .
5.
are
barking outside.
D.
Add subjects
Answers
1.
I
2.
Army
3.
Birds
4.
The players
5.
The thief
Match the following
1.
C
2.
A
3.
E
4.
B
5.
D
A.
Pick out Phrases or Clauses
from the following sentences :
1.
This is the boy
who topped the class.
Clause
2.
At sunset,
they returned
home.
Phrase
3.
The tops of mountains were
covered with snow.
Phrase
4.
A group of girls were sitting
on the bench.
Phrase
5.
We can not play
while it is raining.
Clause
6.
I went to bed at nine
o’clock.
Phrase
B.
Make sentences :
1
In the evening : I go for a
walk in the evening.
2.
While I am having lunch: My brother is watching
TV while I am having lunch.
3.
Who helps themselves: God helps those who help
themselves.
4.
Over the bridge :The helicopter is flying over
the bridge.
5.
Who speaks English fluently: she is the girl who
speaks English fluently.
C:
C.
Make five phrases and use them in
sentence :
1.
The sun rises in the east.
2.
The sun shines brightly in
the afternoon.
3.
There are some clouds in the
sky.
4.
We are basking in the sun.
5.
The sun always sets in the
west.
A.
Choose the correct
option: Answers:
1.
B
2.
A
B.
Write the following sentences in another way :
1.
–
2.
She did nothing.
3.
He can play neither cricket
nor table tennis.
4.
His father can
neither read nor write.
5.
They can give you no more money.
C.
Change the following sentences into Affirmative
sentences
1.
Mohan saw it
everywhere.
2.
There is some
water in the bucket.
3.
I know everything about him.
4.
She can play either chess or
carrom.
5.
He always comes in uniform .
Page 18
Exercise A
Answers:
1.
A
2.
B
3.
B
Ex B
Answers:
1.
Which
2.
Which
3.
What
4.
What
5.
Which
6.
How
7.
Who
8.
What
Exercise C
Change the following statements into questions.
9.
Does your uncle
read the Hindustan Times?
10.
Do they like to fly kites?
11.
Does Rohan like
to watch the Discovery channel ?
12.
Does he have a brother and a
sister?
13.
Did they attend the seminar on
globalisation?
Exercise
A.
Answers
1.
B
2.
A
Ex B
Answers
Choose one word noun from the box—————-words.
1.
Bankrupt
2.
Omniscient
3.
Pedestrian
4.
Feminist
5.
Teetotaller
6.
Spinster
7.
Fatalist
8.
Orphan
9.
Conspirator
10.
Philanthropist
Put these collective nouns in the
blanks below
1.
Flock
2.
Crew
3.
Committee
4.
Fleet
5.
Herd
6.
Mob
7.
Regiment
8.
Team
9.
Jury
10.
Swarm
D.
Match the following
1.
A
group of beautiful ladies
2.
A
bunch of flowers
3.
A
group of people assembled for religious worship.
4.
A
group of soldiers.
5.
A
large noisy
crowd of people.
6.
A
group of players.
7.
A
group of lions.
8.
People gathered for a specific purpose,
9.
A
group of fish swimming together.
10.
A
group of directors or members
E.
Classify the underlined nouns
Answers
1.
Proper
/collective/common
2.
Collective
3.
Abstract
4.
Common
5.
Proper/common
6.
Abstract
7.
Common/collective/common
8.
Abstract
9.
Material
10.
Material
11.
Abstract /abstract
12.
Proper/abstract
13.
Abstract
14.
Common
15.
Common
Pick out odd one out
1.
Chair
2.
Capsicum
3.
Bag
4.
Pizza
5.
Fox
G. (1)
Form the abstract noun
1.
Perfection
2.
Imagination
3.
Invitation
4.
Education
G. (2)
Form abstract noun by adding – ment
1.
Appointment
2.
Payment
3.
Treatment
4.
Movement
G.( 3)
Form abstract noun by adding. (Ity)
1.
Humanity
2.
Stupidity
3.
Reality
4.
Generosity
G (4)
Form abstract noun
1.
Wisdom
2.
Theft
3.
Gentleness
4.
Behaviour
5.
Presence
6.
Success
7.
Loser
8.
Justice
9.
Activeness
10.
Tension
H. Use suitable abstract noun from
the box
1.
Patience
2.
Courage
3.
Desire
4.
Inspiration
5.
Anger
Learner’s drill
Across
1.
Crowd
2.
Herd
3.
Pile
4.
Suite
5.
Bunch
6.
Team
Down
1.
Shoal
2.
Army
3.
Crew
4.
Bouquet
Class - 6
English Reader
Chapter – 1
Part -D
Think and answer
1ans
. The Jungle life was very organised . There were proper
rules for eating, hunting and talking with other species .
There were rules for what to do and what not to do.
2
ans.
Yes,
the animal shared a friendly and loving relationship with
Mowgli because Mowgli followed the rules of animals . He
lived the same way as other animals lived.
Word study
E part
·
Sound
: Whooping, Screeched , yelling
·
Movement : Nimble, Swooped, Fluttering
F part – fill in the blanks
1 ans. Yelled
2 ans . Nimble
3 ans. Screamed
4 ans. Bounded
5 ans. Fluttering
6 ans. Swooped
7 ans. Whispered
8 ans. Screeching
G
part – Rewrite
1 ans . Andy worked very hard at
the restaurant for months before he got his break as an
actor.
2 ans. My feet are paining a lot.
3 ans. Alia had a wide beaming
smile when she heard the news.
4ans . Puneet cried a lot when he
lost the game.
5 ans. Harpreet took a long time to
complete the work.
6 ans. We would often laugh a lot
at her jokes.
7 ans. Gunjan was feeling very
nervous as she approached the principal’s office.
H part – Dictionary
1 ans. Amiable
2 ans. Average
3 ans. Advice
4 ans . Agreement
5 ans. Anecdote
6 ans. Aquatic
Grammer study
|
Noun
|
Verbs
|
Adjective
|
Preposition
|
|
Ranji
|
Rising
|
Distant
|
On
|
|
Grass
|
Play
|
Smaller
|
Against
|
|
Sun
|
Looking
|
Friendly
|
In
|
|
Hills
|
Met
|
Full
|
Behind
|
|
Flower bed
|
Held
|
Wet
|
With
|
J part – partsof speech
1 ans. Noun
2 ans. Pronoun
3 ans. Adjective
4 ans. Verb
5 ans. Adjective
6 ans. Preposition
7 ans. Conjunction
8 ans. Article
Class
6 Civics
1.Tick(✓)the
correct answer.
Ans:1 Three-tier system
Ans:2 18 years
Ans:3 supervises the working of block samitis
Ans:4 Nyaya panchayat
Ans:5 Zila parishad
2.Fill in the blanks
Ans:1 five
Ans:2 gram sabha
Ans:3 punishes
Ans:4 Democracy
Ans:5 5years
Ans:6 block
Ans:7 supervises
Ans:8 panchayat secretary
3.Match the column
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 1
(d) 5
(e) 2
4.True or False
1. True
2.True
3.True
4.False
5.True
6.True
7.True
5.Answer the following questions.
Q.1 What do you mean by 'Panchayat?
Ans: The rural local self-Government formed a group of five
members elected
by the
Villagers is known as Panchayat.
Q.2 Explain the importance of local self- Government?
Ans: Local self-governing bodies develop
local leadership that later helps the
state and Central governments in
sharing the burden of work which thus
gets done quicker, better and cheaper.
Q.3 Name the three institutions of the Panchayati Raj. At
what level do the
Work?
Ans:(a)At the lowest level there is Village Panchayat.
(b)At the block level there is
Panchayat Samiti.
(C)At the district level there is
Zila Parishad.
Q.4 Explain berify the composition and unctions of a
block Samiti?
Ans: The pradhans and panchas of the Village Panchayats in
a block choose
their representatives to the block Samiti.
Besides such representatives,there
are
Other members as well. The members elect a chairperson
and a vice
chairperson.
Functions of block Samiti :-
1. A block Samiti supervises the working of the
village Panchayats.
2. It arranges funds from the government
for the block development programmes.
3. It makes plan in agriculture,construction
of roads and buildings,health and education etc.
Q.5 How is zila Parishad formed ? What are
its main functions?
Ans:The zila Parishad coordinates the activities of
the block Samitis in the
Whole district.The zila Parishad elects
a president and a vice-president from
among its members.
Functions :-
1. The main function of the zila Parishad is to
see that Village Panchayats and
block Samitis work properly.
2.The zila Parishad also has the responsibility of
implementing various
Programmes.
3.The zila Parishad also prepares and
executes development plans for district.
Class -6
English
Novel
Chapter - 2 Joe Green
A.
Comprehension
Read chapter 2 and write true and false.
·
1.Ginger is unhappy
because people hurt her in the past.
True
·
2. Joe
Green is the new stable boy at Birtwick.
True
·
3. John wakes Ginger up in
the middle of the night.
False
·
4. Squire Gordon rides
black beauty to get the doctor.
False
·
5. Black Beauty gets
better quickly from his illness. False
·
6. Joe’s father ask John
to be kind to Joe. True
B.
What do you think?
·
In what way is Ginger's
attitude to Black Beauty different now? What do you think
caused this change?
Ans. Ginger and Black Beauty pull
the carriage together . It was easy for Black Beauty to work
with Ginger. they soon became friends.
·
Why
do you think Squire
Gordon Sends John instead of Joe to get the doctor?
Ans. Squire Gordon Sends John
instead of joe to get the doctor because Joe was a new boy
in the stable .He was very young and he did not know much
about the horses.
·
How does Joe feel when
Black Beauty becomes ill? Do you think it is His fault?
Ans. Joe feels sad and things it
was his fault. I think Joe green did not know much about the
horses. He gave Black Beauty cold water to drink and did not
put warm blanket on his body but he was not a bad boy .He
did his best to take care of Black Beauty.
·
Why does Joe's father go
and talk to John? What do you think of him as a parent?
Ans. Joe was feeling guilty for
not taking care of Black Beauty properly . He could not eat
and smile. Joe’s father talk to John
He
want to john on to say kind words to joe.
As
a parent I think joe was not a bad boy . He did his best to
take care of Black Beauty.
C.
Language practices.
1.Write word and make sentences
1.
Kind
word : Joe wanted to hear some kind words from
John.
2.Friendly
people : Black
Beauty always met friendly people.
3. Cold
water : Joe gave
Black Beauty cold water to drink.
4.
Horse doctor: The horse
doctor came to treat Black Beauty.
5.
Warm
blanket: Joe
didn’t put warm blanket on Black Beauty.
6
Good
friends: Ginger and
Black Beauty became good friends.
7.
Stable
boy: Joe was the
new stable boy.
8.
Long
time: Black Beauty
fell I’ll for a long time.
2. Write paragraph
Squire Gordon gave a note to John
to give it to the doctor. Doctor's horse was lame . So,
Black Beauty carried the doctor to Birtwick . The doctor was
heavy and he did not ride well . Black Beauty got tired and
his legs were wet and he got ill.
Class -6 Biology
Ex. F-Short answer questions:
Chapter 6
Ans1-The device used by doctors to listen to our heartbeat
is stethoscope.
Ans2-The main function of the heart is to pump blood.
Ans3-Pulmonary artery carries carbon dioxide- rich blood.
Ans4-Pulmonary vein carries oxygen-rich blood.
Ans5-Aorta is the largest artery in the human body.
Ans6-White blood cells are important for immunity.
Ans7-Valves in veins allow blood to flow only towards the
heart.
Ans8-Blood will not clot if the blood platelets count drops
in a human being.
Ans9-The functions of blood in our body are-
(1) It regulates our body temperature.
(2) It transports nutrients to various parts of the body.
Ans10-Arteries have thick elastic walls because blood flows with pressure
in them.
Ans11-Throbbing felt in the artery due to pumping action of heart is
called pulse.
Ans12-Blood group O is a universal donor.
Ans13-Rh-positive blood group means Rh factor is present on the red blood
cells.
Ans14-Person with blood group A can receive blood from blood group A and
O only.
Ex-G (HOTS):
Ans1-Doctors inject medicines in the veins because veins are
often superficial and close to the surface than arteries.
Moreover, veins carry blood to the heart from where it is
distributed everywhere.
Ans2-Capillaries do not have valves because blood pressure in arteries is
sufficient to allow the blood flow in one direction.
Ans3-The four chambered heart prevents the mixing of oxygenated and
deoxygenated blood.
Class -6 Geography
Chapter 1 Globes and Maps
1. Fill ups
a.axis
b. Direction
C.
Cardinal
D.legends
e.heights and depths
f.contour
line
g.sketch
h.meander
2. Match the following
A=7
B=8
C=5
D=4
E=3
F=2
G=1
H=6
3.True and false
A. F
B. T
C. F
D. T
E. F
F. F
G. F
H. F
I.
4. Choose the correct answer
A.3
B.1
C.1
D.2
5. Short answer
Answer A.A
Globe is a model of the earth .
Answer B. A map is
symbolic representation of the earth or apart of it on a
flat surface made true to scale.
Answer C. The different
types of the maps based on scale are large scale map and
small scale map.
Answer D. The ratio between the distance
on a map and the corresponding true distance on the ground.
Answer E. A political map is used to show countries capitals
and its boundaries.
Answer F.Distance directions and
conventional signs and symbols are used to understand maps
well.
Answer G.The colours used in maps are red, blue,
green, yellow ,brown and black.
Answer H. A sketch is a
rough drawing of an area.
Answer I.Two ways by which
signs and symbols can be shown are keys and legends.
Answer J. Plans are used to shows detailed features of a
small area or building.
Answer k. Anticline-It is an up
fold in rocks resulting from compressive stresses in the
Earth’s crust.
Syncline-. It is downfold in rocks
resulting from compressive stresses in the Earth’s crust.
Answer L. A block mountain is formed due to forces of
compression or tension.
6. Answer the following in
details
Answer A. The disadvantages of using a globe are
1. It is difficult to carry around.
2. A part of earth is
visible at a time.
3. Unable to provide detailed
information on a large scale.
Answer B.The uses of a map
are
1.Geographer use it to get detailed information about
an area .
2. City planners decide where to put the
hospital, Park etc.
3. Tourists and navigators use it to
find their way to their destination.
4. It is very
important for the defence department to have information of
the border areas.
Answer C. Differentiate between the
following
1.Large-scale map and small-scale map
Large-scale map- A large scale map shows a large amount of
detail while representing a limited area such as
neighbourhood or towns.
Small-scale map-A small-scale map
shows a small amount of detail over a wide area such as the
word.
2. Contour lines and Isotherms
Contour lines -
contour lines join places that are of the same height.
Isotherms- Isotherms join places that experience similar
temperatures.
3. A Sketch and a Plan
A Sketch-A sketch
is a rough drying of an area.
Plan- A fairly accurate
drawing that shows detailed features of an area or building.
Answer D. The importance of direction and distance Is if we
need to locate a place then we need to know both its
direction and distance from a given point.
Answer E.
Conventional signs and Symbols are useful to indicates
various features in a clear and Simple manner in the limited
space of map.
Answer F. Colour can be used to display the
different heights of landforms or depths of water bodies.
Different colours represent different physical features.
Eg. Blue colour is used to denote water bodies .
Class 6 Mathematics
Chapter 1
Exercise1.1
Q1)
1. Four lake twenty seven thousand three hundred
twenty.
2. Eight million one hundred fifty two thousand
three hundred sixty seven.
3. Seventy eight core twenty
nine lakh fifty three thousand four hundred twenty nine.
4. Four hundred ninety two million three hundred one
thousand four hundred six.
Q2)
1. 83,56,407
2.
2,01,93,256
3. 4,06,70,983
4. 70,23,91,783
Q3)
1. 40,693,207
2. 10,239,743
3. 409,762,320
4.
572,369,406
Q4)
1. Four hundred seventy three million
five hundred two thousand one hundred three.
2. One
hundred ninety two million three hundred four thousand six
hundred ninety three.
Q5)
1. 7,45,060
2.
90,20,04,701
3. 105,067,009
4. 90,000,004
Exercise - 1.2
Q1)
1. 7000 , 7
2. Place value = 3
Face value = 3
Difference = 3 - 3 =0
Q2)
1. Place value = 70000
Face value = 7
2. Place value = 50
Face value = 5
Q3)
Place value = 80000
Face value = - 8
Difference
= 79992
Q4)
1. 70000+0+5000+900+20+3
2.
5000000+600000+0+2000+300+70+9
Q5)
1. 70,549
2.
90,400,206
Exercise -1.3
Q1)
1. Greatest number =
75320
Smallest number = 20357
2. Greatest number =
97431
Smallest number = 13479
Q2)
Greatest number =
98765432
Smallest number = 10234567
Q3)
Largest
seven digit number=9999999
Smallest seven digit no.=
+1000000
Sum = 10999999
Q4)
444, 466, 499, 469,
446, 449, 464, 494.......
Q6)
1. 535
2. 43138
3.
12304
Q7)
109, 304, 329, 507, 947, 4993
Q8)
47320, 29761, 7259, 5554, 153
Q10)
1. S = 1000 P = 998
2. S = 401 P = 399
3. S = 63100 P = 63098
4. S = 10001
P = 9999
Q11)
Greater number = 13,98,357
Difference
= 9,83,563
Smaller number = 13,98,357-9,83,563
=
4,14,794
Q12)
Total Population = 9,75,165
Number of
teachers= 9,75,165÷15
= 65,011
Q13)
Product of two
numbers= 4,35,375
One number = 225
Other number =
4,35,375÷225
= 1935
Class 6 Chapter 1
English
literature [Reader book]
Mowgli in
trouble
Comprehension
A.
Write true and false
·
The Bandar – log took Mowgli to the rainforest.
False
·
Bagheera taught Mowgli the ways of the Jungle.
False
·
The monkey people were happy to have Mowgli among them.
True
·
Bagheera and Baloo were the first to reach the cold lairs.
False
·
Baloo and kaa freed Mowgli from the room where he was
trapped.
False
B.
Who said these words, to whom and why?
·
“Tell
Baloo and Bagheera where they are taking me! ”
Ans.
Mowgli said to Rann the kite because he wanted them to come
and rescue him.
·
“ It is
the Bandar log that we follow. ”
Ans.
Baloo said to Kaa. He wanted kaa to help them to get Mowgli
free from monkeys.
·
“ we are
of one blood . I owe you my life tonight. My kill shall be
yours if you are ever hungry. ”
Ans.
Mowgli said to Kaa because he freed him from monkeys.
C.
Answer these questions.
·
Why did
the bandar log kidnap Mowgli?
Ans. They
wanted him in their tribe and to make Mowgli the leader of
Bandar log.
·
Who help
did Baloo and Bagheera seek to bring Mowgli back. Why?
Ans.
Baloo and Bagheera seeked the help of kaa because kaa was
the only animal that the monkeys feared in the jungle.
·
How did
the Bandar log behave when Mowgli was among them?
Ans. The
monkeys were
very pleased . They clapped and danced about . They sang
their foolish songs.
·
What made
Mowgli think that the Bandar log were a foolish and silly
tribe?
Ans.
Mowgli tried to teach them how to weave sticks and canes
together for protection against rain and cold .Some
tried to imitate Mowgli but some lost interest and began to
pull tails of each other and jump up and down . They were
not interested in learning anything . So Mowgli thought they
were silly and foolish.
·
Describe
Kaa's attack on the monkeys . Why did the monkeys fear him
so much?
Ans. Kaa
was 30 feet long . He gave a strike into the crowd of
monkeys . The monkeys scattered with cries of Run Run .
The
monkeys feared Kaa as they knew his powers
were limitless. They know that none had ever come
alive out of his hug.
·
How did
Mowgli express his gratitude towards Kaa?
Ans.
Mowgli told Kaa that we are of one blood and that he owed
Kaa his life.
He told
Kaa that he can do hunting for him and can also free him if
he is ever caught in a trap.
Class 6 English language Chapter 4
A. Choose
the correct option:
Answers:
1. B 2. A
B. Write the following sentences in another way :
1. – 2. She did nothing. 3. He can play neither cricket
nor table tennis. 4. His father can neither read nor write.
5. They can give you no more money.
C. Change the
following sentences into Affirmative sentences
1.
Mohan saw it everywhere. 2. There is some water in the
bucket. 3. I know everything about him. 4. She can play
either chess or carrom. 5. He always comes in uniform .
Page 18 Exercise A
Answers:
1. A 2. B 3.
B
Ex B Answers:
1. Which 2. Which 3. What 4.
What 5. Which 6. How 7. Who
Class 6. English Language
Chapter 3
A. Pick out Phrases or Clauses
from the following sentences :
1. This is the boy
who topped the class. Clause 2. At sunset, they returned
home. Phrase 3. The tops of mountains were covered with
snow. Phrase 4. A group of girls were sitting on the bench.
Phrase 5. We can not play while it is raining. Clause 6. I
went to bed at nine o’clock. Phrase
B. Make
sentences : 1 In the evening : I go for a walk in the
evening. 2. While I am having lunch: My brother is watching
TV while I am having lunch. 3. Who helps themselves: God
helps those who help themselves. 4. Over the bridge :The
helicopter is flying over the bridge.
5. Who speaks English
fluently: she is the girl who speaks English fluently.
C: C. Make five phrases and use them in sentence :
1. The sun rises in the east. 2. The sun shines brightly
in the afternoon. 3. There are some clouds in the sky. 4. We
are basking in the sun. 5. The sun always sets in the west.

Chemistry Chapter no -1
Introduction to chemistry
1Q select the correct option:
1. a
2. c
3. c
4. a
5. a
2Q . Fill in the blanks:
1. Fertilisers
2. Gas jar
3. China dish
4. Insecticides
5. Joseph priestley
3Q True or False
1. True
2. False . Prevent the growth of microorganisms.
3.False. Ernest Rutherford discovered atomic nucleus.
4.True
5.True
4Q Match the following:
1. b
2. d
3. e
4. a
5. c
Understanding ideas
1.Answer in one word:
1. John Dalton
2. Inorganic chemistry
3. Measuring cylinder
4. Trinitrotoluene
5. Conical
|

